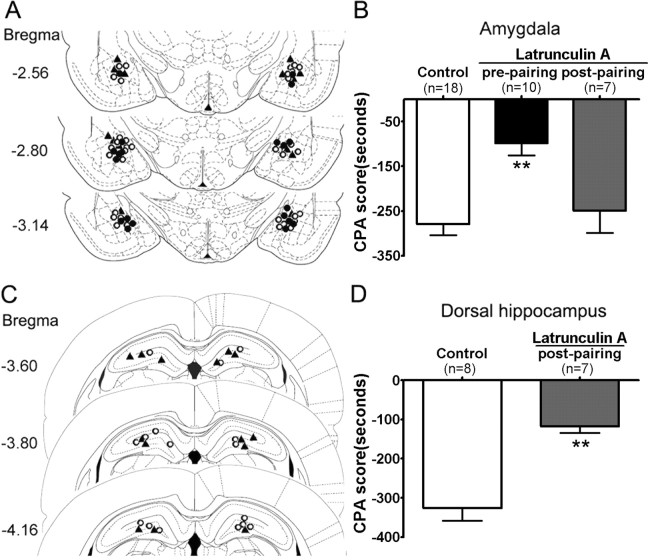
Figure 5.
Effects of intra-amygdala or intra-DH injections of latrunculin A, an inhibitor of actin polymerization, on place aversion induced by conditioned drug withdrawal after exposure to a single dose of morphine. Left column, Schematic representation of injection sites in the amygdala (A) and the DH (C) for rats used in the experiments (○, control; •, latrunculin A injected before pairing; ▴, latrunculin A injected after pairing). Right column, B, Prepairing but not postpairing intra-amygdala injection of latrunculin A attenuated place aversion induced by conditioned naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal in the acute morphine-dependent rats. Latrunculin A (250 ng/0.5 μl per side) or vehicle (0.5 μl/side) was bilaterally microinjected into the amygdala 10 min before pairing or immediately after pairing with morphine withdrawal. D, Postpairing intra-DH injection of latrunculin A attenuated place aversion induced by conditioned naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal in the acute morphine-dependent rats. Latrunculin A (500 ng/1 μl per side) or vehicle (1 μl/side) was bilaterally microinjected into the DH immediately after pairing with morphine withdrawal. Values are represented as the mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01, compared with the corresponding vehicle-microinjected control group, Student's t test or one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test.