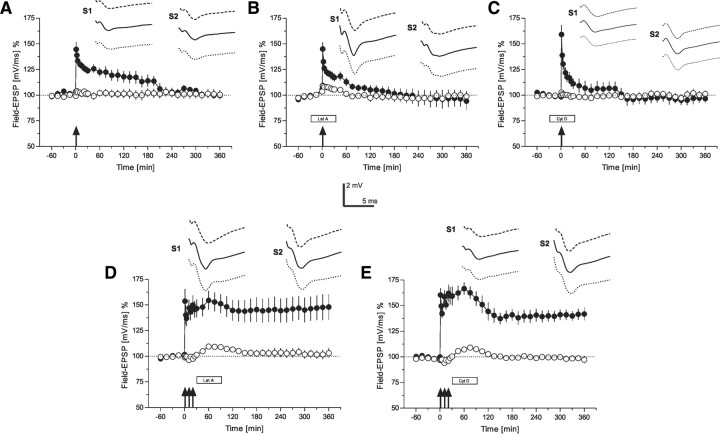
Figure 2.
The role of the actin network for early-LTP (time courses of field EPSP recordings). A, Time course of the slope of field EPSP after the induction of early-LTP by WTET (indicated by the single arrow) in S1 (filled circles). The control pathway S2 (open circles) remained stable throughout the experiment (n = 7). B, The influence of latrunculin A on early-LTP: the drug was applied 30 min before WTET of S1 (filled circles; open circles represent the time course of the control input S2; n = 7). C, Similar to B, but now instead of latrunculin A, cytochalasin D was applied 30 min before WTET of S1 (filled circles; open circles represent the time course of the control input S2; n = 7). D, The effect of latrunculin A on late-LTP if applied 30 min after STET in S1 (filled circles). Open circles represent the time course of the control input S2 (n = 6). E, Similar to D, but instead of latrunculin A, now cytochalasin D was applied (n = 7). The time points of the analog traces as well as the calibration as in Figure 1. Arrows indicate the time point of tetanization (STET are symbolized as 3 arrows, WTET by a single arrow, were appropriate). Boxes as in Figure 1.