Figure 2.
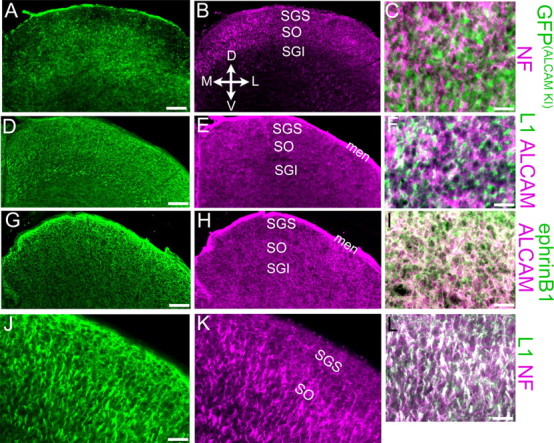
ALCAM is expressed by cells of the superior colliculus. Immunostaining of P2 WT (D–L) or ALCAM+/− (A–C) superior colliculus using antibodies against ALCAM, GFP (to detect its expression from the ALCAM locus in ALCAM+/− mice), NF, L1, or EphrinB1 is shown in representative coronal cryostat sections. Coordinates for all panels are indicated in B; midline is at or near the left edge of each panel. GFP expressed from the ALCAM locus [GFP(ALCAMKI)] in heterozygotes labels cell bodies near the SO and in deeper layers of the SC, including those in contact with NF-labeled RGC axon bundles within the SO (note apposition but little overlap in the higher magnification merge; C). D–F, In WT SC, ALCAM protein is diffusely distributed throughout the neuropil, including that innervated by L1-positive axon bundles in the SO; the merged image (F) shows ALCAM protein adjacent to, but mostly excluded from, these L1-positive axons. ALCAM and EphrinB1 exhibited extensive colocalization in the SC neuropil (seen as white staining in the merged panel; I), although EphrinB1 was more prominent in the upper SGS than was ALCAM (G, H). J–L, L1 protein was primarily found on NF-positive RGC axon bundles in the SO (white staining in the merged panel; L), although some NF-negative L1 staining, presumably from intrinsic SC cells, was observed in the SGS (J). D, Dorsal; V, ventral; M, medial; L, lateral; men, meninges. The sections in A–F are from the rostral SC; those in G–L are from approximately midway through its rostrocaudal extent. Scale bars: A, B, D, E, G, H, 100 μm; J, K, 40 μm; C, F, I, L, J, 25 μm.
