Figure 7.
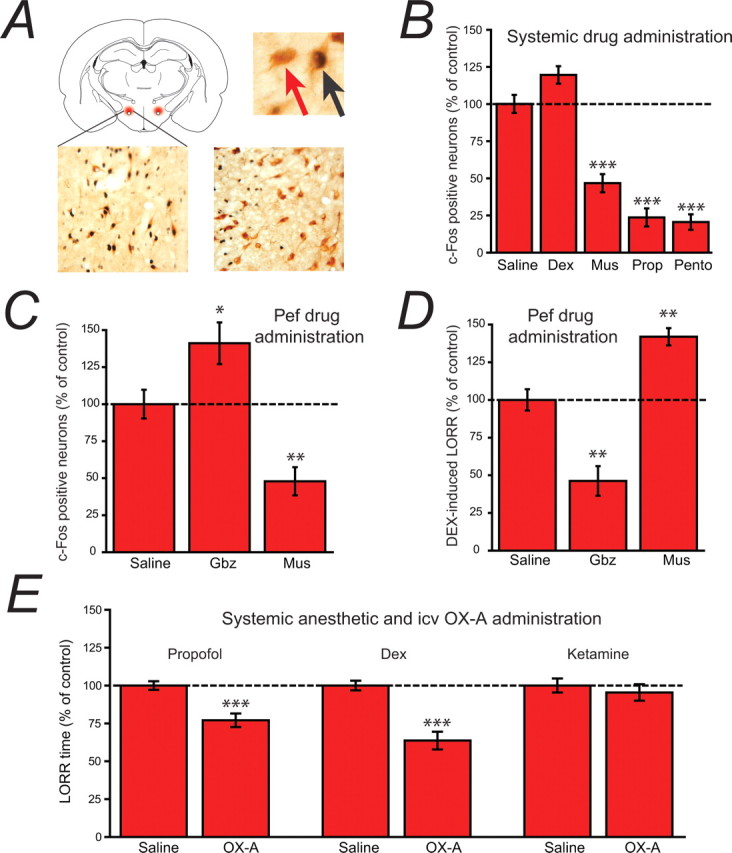
Evidence for the involvement of orexinergic neurons in anesthetic-induced LORR. A, The schematic coronal slice (top left) shows the location of Pef orexinergic neurons (red) close to the fornix. The image top right shows 3,3-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride-visualized neurons, double-stained for cytosolic orexin-A (brown) and nuclear c-Fos (black). The red arrow points to a single-labeled orexinergic-positive, but c-Fos-negative neuron and the black arrow indicates a double-labeled c-Fos-positive orexinergic neuron. The lower images show (left) a level of c-Fos expression in orexinergic neurons following systemic dexmedetomidine (Dex; 150 μg/kg) that is similar to control levels, in contrast to the marked depression of c-Fos expression observed (right) following pentobarbital administration (Pento; 50 mg/kg). B, C-Fos-positive neurons following systemic administration of dexmedetomidine (Dex; 150 μg/kg, i.p.), muscimol (Mus; 5 mg/kg, i.p.), propofol (Prop; 100 mg/kg, i.p.) and pentobarbital (Pento; 50 mg/kg, i.p.) expressed as a percentage of those observed following saline administration. Following saline injection, 47.8 ± 2.9% of orexinergic neurons were c-Fos positive. C, When administered directly into the Pef (bilateral injections, 0.2 μg/0.2 μl/side), the GABAA receptor antagonist gabazine increases c-Fos expression in orexinergic neurons, whereas the GABAA receptor agonist muscimol decreases expression compared with the injection of control saline (normalized to 100%; 45.5 ± 4.4% of neurons were c-Fos positive), showing that the activity of Pef neurons can be modulated by GABAergic agents. D, When administered directly into the Pef (bilateral injections, 0.2 μg/0.2 μl/side), gabazine antagonizes Dex-induced LORR (150 μg/kg, s.c.), whereas muscimol significantly increases Dex-induced LORR compared with the injection of control saline (normalized to 100%; control sleep time was 286 min), showing that the modulation of Pef neurons can directly influence LORR. Significance was tested using an unpaired Student's t test. E, The intracerebroventricular administration of orexin-A significantly antagonizes propofol and dexmedetomidine anesthesia, but has no effect on ketamine anesthesia compared with the intracerebroventricular injection of saline. In each case the mean control sleep times have been normalized to 100% (control sleep times were 8.2 min for Prop, 26.2 min for Dex and 3.6 min for ketamine). Significance was tested using a paired Student's t test with respect to control saline injections on the same animal. The data are means ± SEMs, and the asterisks denote the level of significance (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).
