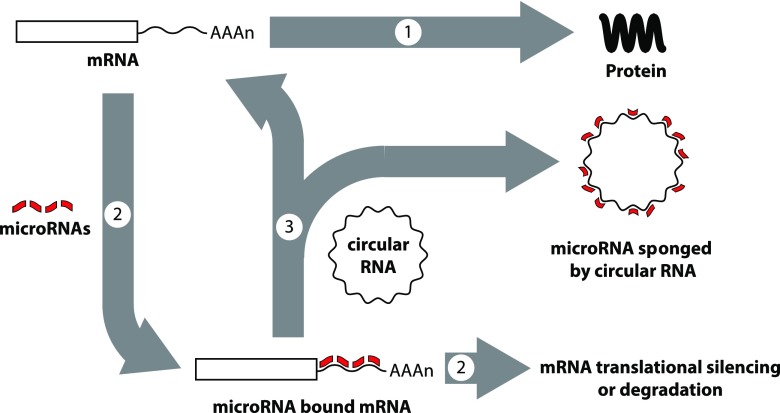
Fig. 8.
Post-transcriptional gene regulation by microRNAs and circular RNAs. Gene expression involves translation of mRNAs to proteins (arrow 1), but the process can be blocked when microRNAs bind to mRNAs through sequence complementarity (arrow 2). Depending on the microRNA sequences and the presence or absence of bulges in the binding due to the presence or absence of perfect matches in complementarity, mRNAs may become translationally silenced or targeted for degradation (arrow 2). However, circular RNAs also can bind and sequester microRNAs, lowering their ability to target mRNAs, a process termed sponging, which can block the inhibitory effects of microRNAs (arrow 3).