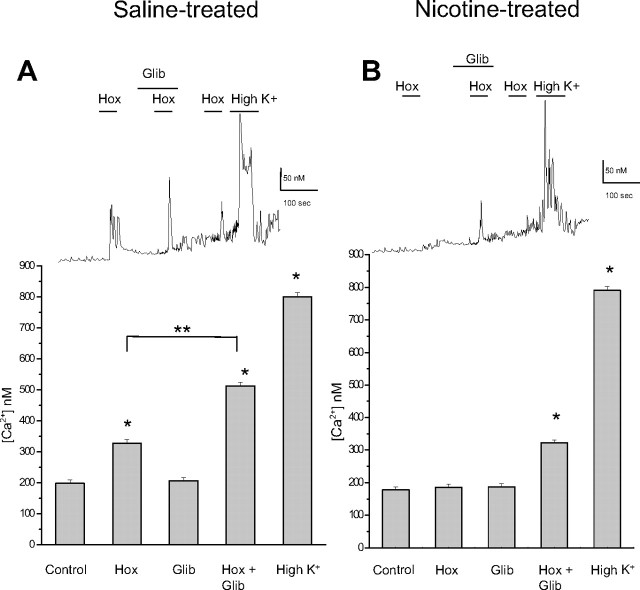
Figure 3.
Fura-2 spectrofluorimetric determination of intracellular calcium (Cai) levels in AMCs derived from P0 pups born to saline-treated versus nicotine-treated dams. In P0 saline-treated AMCs, significant increases in Cai relative to normoxic (Nox) control (ANOVA; *p < 0.001) occurred during exposure to hypoxia (Hox) (PO2 ∼ 15 mmHg) and the depolarizing stimulus, high extracellular K+ (30 mm). Although the KATP channel blocker glibenclamide (glib) had no effect on its own, it significantly potentiated the hypoxia-induced rise in Cai seen in saline-treated cells as illustrated in the histogram in A (significance compared with hypoxia alone, **p < 0.001, n = 42). Comparative data are shown for nicotine-treated AMCs in B (n = 35). Note lack of effect of hypoxia alone on Cai levels in nicotine-treated AMCs, although coapplication of glibenclamide and hypoxia resulted in a significant increase in Cai (ANOVA; *p < 0.001). Error bars indicate SEM. Sample recordings are shown in the top traces.