Figure 7.
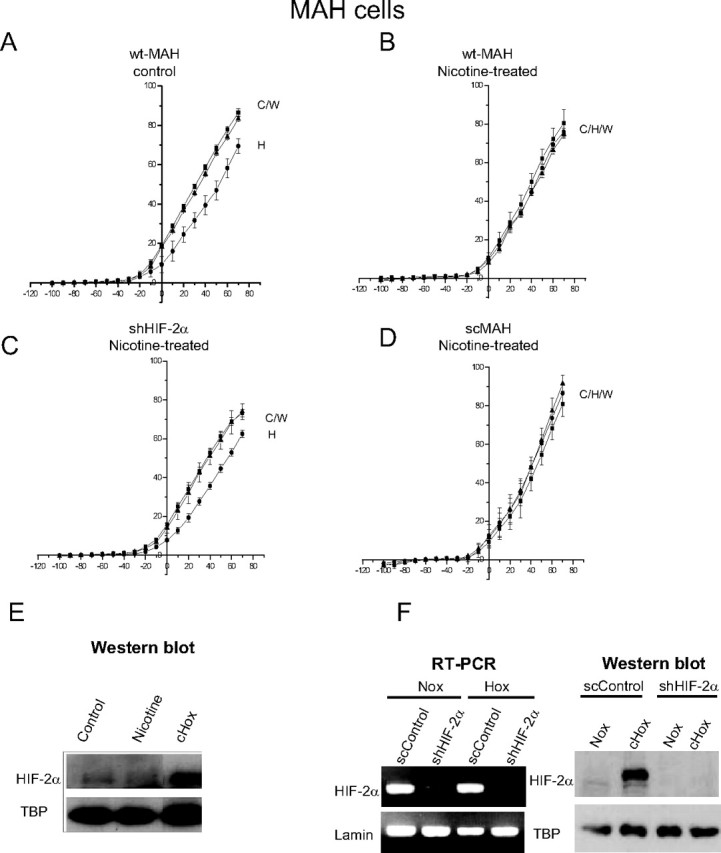
Role of HIF-2α in mediating the nicotine-induced loss of hypoxia sensitivity. MAH cells deficient in HIF-2α (>90% knockdown) (shMAH) were cultured with or without nicotine, and hypoxic sensitivity was determined based on inhibition of outward K+ current. Control, wild-type MAH cells (wtMAH) were hypoxia-sensitive (A) but became hypoxia-insensitive when cultured with chronic nicotine (B). In contrast, nicotine treatment failed to affect the hypoxic sensitivity of MAH cells deficient in HIF-2α (shMAH) (C); however, in scrambled control MAH cells (scMAH), nicotine exposure still resulted in a loss of hypoxic sensitivity (D). Error bars indicate SEM. In E, the Western blots show that HIF-2α protein was induced in MAH cells by chronic hypoxia (CHox) (2% O2 for 24 h), but not by chronic nicotine; HIF-2α induction by chronic hypoxia was also present in scMAH cells but was absent in shMAH cells (F). RT-PCR analysis in F shows downregulation of HIF-2α mRNA in shMAH cells, but not in scMAH cells.
