Figure 4.
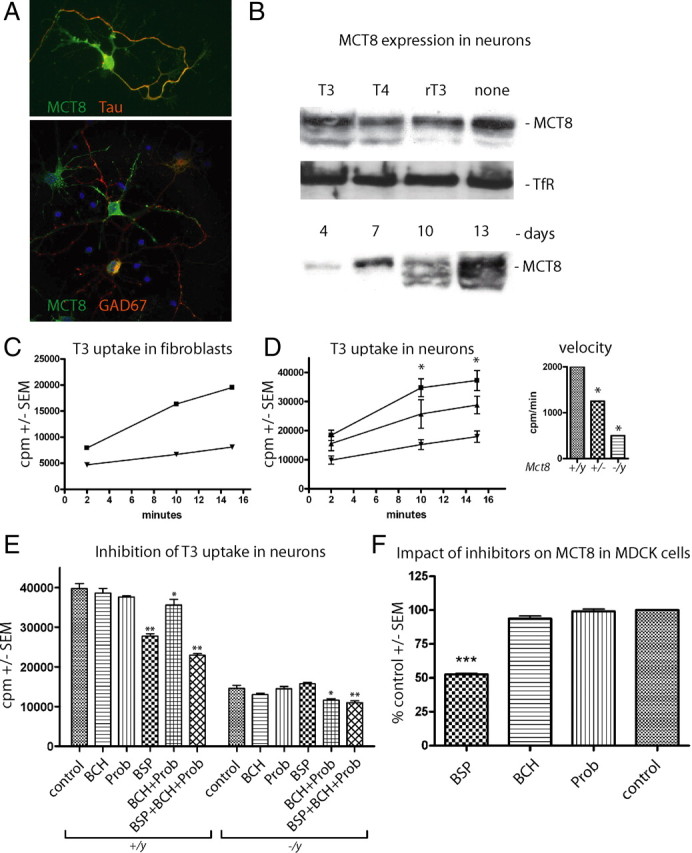
Functional characterization of T3 transporters in primary cortical neurons. A, Primary cortical neurons were cultured for 7 d in vitro and immunostained for Mct8, the axonal marker Tau, and the interneuron marker GAD67. B, Western blot for Mct8 from primary cortical neurons cultured in vitro with the indicated iodothyronines at 10 nm. TfR served as control. C, Kinetic analysis of 125I-T3 uptake in mouse embryonic fibroblasts derived from control (■) and Mct8 −/y (▼) mice. Cell-associated radioactivity (cpm) was measured in triplicate. Error bars (SEM) are smaller than the symbols. D, Kinetic analysis of 125I-T3 uptake in mouse primary cortical neurons derived from wild-type (■), Mct8 +/− (▲), and Mct8 −/y (▼) mice. Cell-associated radioactivity (cpm) was measured in triplicate from two to four independent animals. Error bars denote SEM. Inset, Initial rate kinetics of T3 uptake in relation to Mct8 genotype expressed as cpm per minute. Note that 75% of the T3 uptake rate depends on Mct8. E, Pharmacological inhibition of neuronal T3 uptake reveals Mct8-independent transport. T3 uptake assays were performed in triplicate by addition of inhibitors (1 mm) together with T3. F, BCH and Prob do not inhibit MCT8. Tracer was incubated on MDCK1 cells stably transfected with MCT8 for 4 min and background activity of empty vector-transfected MDCK1 cells was subtracted. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 versus no inhibitor, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's posttest.
