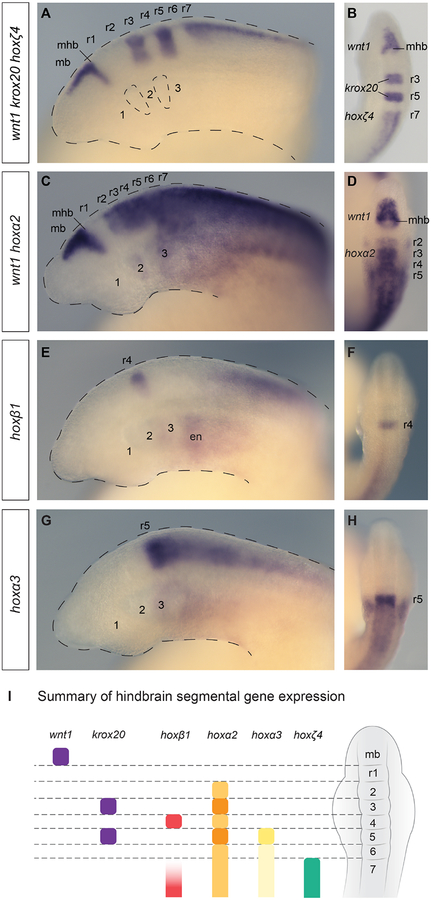
Figure 2: The lamprey hindbrain segmental plan and segmental hox expression.
Lateral (A,C,E,G) and dorsal (B,D,F,H) views of st23.5 lamprey embryos are shown. (A-B) A triple in-situ hybridisation against wnt1, krox20 and hoxζ4 (all purple) demarcates hindbrain segments in the neural tube. wnt1 marks the caudal limit of the midbrain (mb), revealing the midbrain-hindbrain boundary (mhb), while krox20 marks r3 and r5, and hoxζ4 is expressed posterior to the r6/r7 boundary. Rhombomeres (r1–r7) and pharyngeal arches (1–3) are annotated, and the head and pharyngeal pouches are outlined. (C–D) A double in-situ hybridisation against wnt1 and hoxα2, showing segmental hoxα2 expression in the hindbrain posterior to the r1/r2 boundary and wnt1 in the midbrain. hoxα2 is also expressed in the developing pharyngeal arches, posterior to PA1. (E–F) hoxβ1 is expressed in r4 and in the posterior hindbrain/spinal cord, as well as in the pharyngeal endoderm (en). (G–H), hoxα3 shows an elevated stripe of expression in r5, with lower expression levels in the neural tube posterior to r5. Expression is also seen in the pharyngeal arches, posterior to PA2. (I) A depiction of a dorsal view of a st23.5 lamprey embryo, summarising the segmental gene expression domains in the neural tube shown in (A-H), which together demarcate r1–r7.