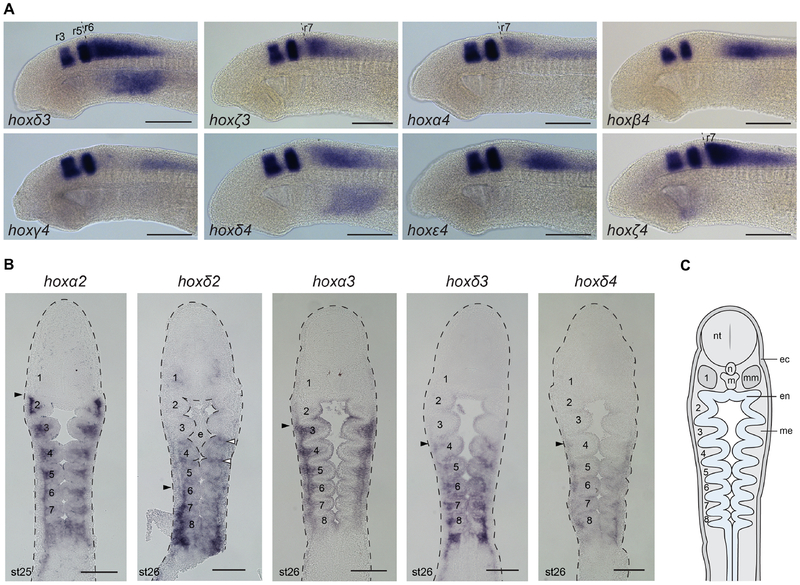
Figure 7: Rhombomeric hoxPG3–4 expression and pharyngeal expression of selected lamprey hoxPG1–4 genes.
(A) Double in situ hybridization of hox genes from PG3–4 with krox20, to resolve rhombomeric expression domains. krox20 expression is in r3 and r5. For the PG3–4 genes with clear rhombomeric boundaries, they are indicated (dashed line). hoxα3 expression in r5 was previously characterized and so is not shown (Parker et al., 2014a). (B) Frontal sections at st25–26, revealing pharyngeal hoxPG2–4 expression domains. Black arrowheads indicate anterior expression limits in the neural crest-derived pharyngeal arch mesenchyme. White arrowheads mark hoxδ2 expression in pharyngeal pouch endoderm. Pharyngeal arches are numbered (1–8). (C) A schematic frontal section of a st26 lamprey embryo indicating the different tissue layers. ec, ectoderm; en, endoderm; m, mouth; me, mesenchyme; mm, mandibular mesoderm; n, notochord; nt, neural tube.