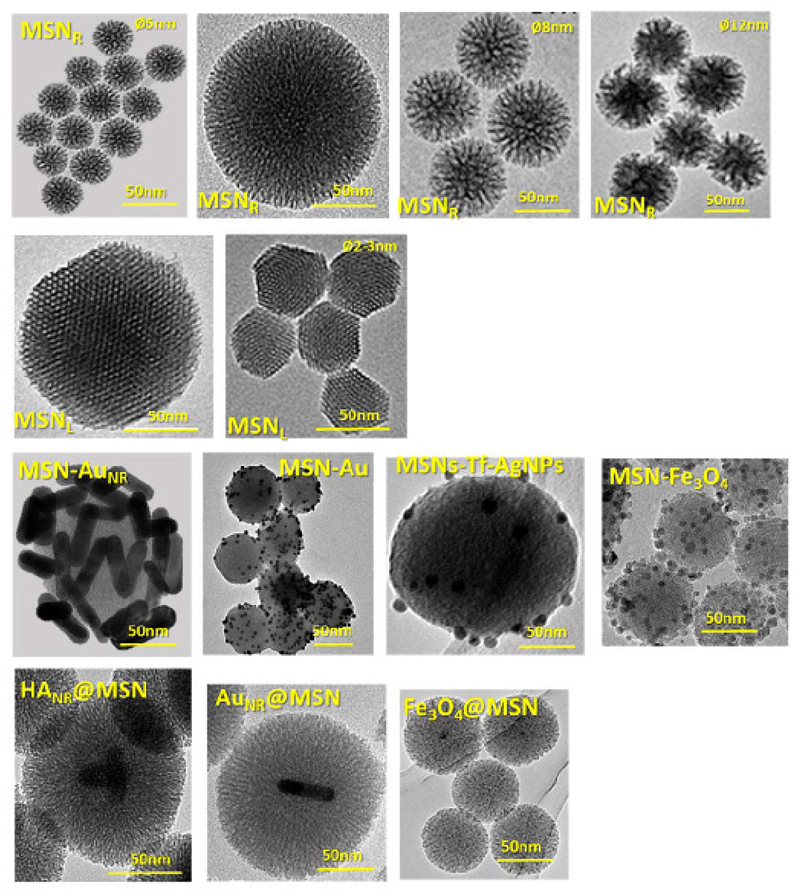
Figure 1.
Transmission electron microscopy of several kinds of MSNs for different biomedical applications, showing (1st row) center-radial porosity (MSNR) with different particle and pore size (2-12 nm); (2nd row) longitudinal or 2D-hexagonal structure (MSNL) with different particle size (150-50 nm); (3rd row) MSNs coated with different inorganic nanoparticles such as gold nanorods (MSN-AuNR); gold nanoparticles (MSN-AuNPs), silver nanoparticles (MSN-AgNPs) and magnetite nanoparticles (MSN-Fe3O4); (4th row) core@shell structure with hydroxyapatite nanorods (HANR), gold nanorods (AuNR) and magnetite nanoparticles (Fe3O4) as core.