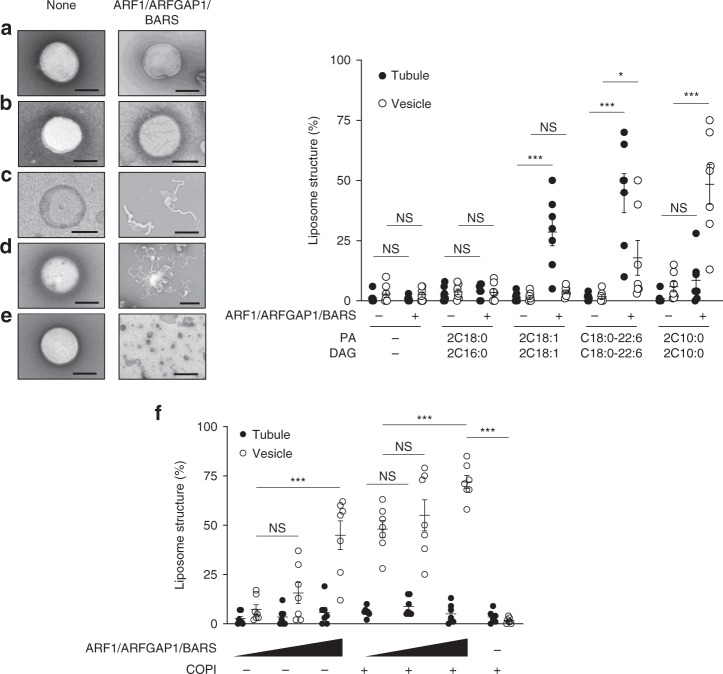
Fig. 6.
Reconstituting vesiculation with liposomes. Quantitative data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. Significance was tested using the two-tailed Student’s t test, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.0001, NS P > 0.05. Golgi-like liposomes were generated with additional lipids incorporated as follows: a none, b phosphatidic acid (PA) (2C18:0) and diacylglycerol (DAG) (2C16:0), c PA (2C18:1) and DAG (2C18:1), d PA (C18:0/C22:6) and DAG (C18:0/C22:6), and e PA (2C10:0) and DAG (2C10:0). Liposomes were then incubated with Coat Protein I (COPI) fission factors as indicated, followed by electron microscopic (EM) examination. Representative images are shown on left, bar = 250 nm. The degrees of liposome tubulation and vesiculation are quantified on right; n = 7 independent experiments. f Golgi-like liposomes with PA (2C10:0) and DAG (2C10:0) were incubated with increasing levels of COPI fission factors (ARF1, ARFGAP1, and BARS) and either with or without coatomer, followed by EM examination to assess the degree of liposome tubulation and vesiculation; n = 3 independent experiments. Source data are provided as a Source Data file