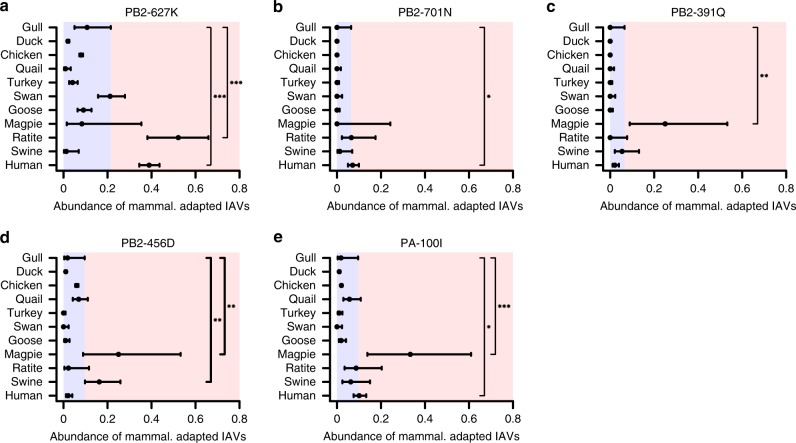
Fig. 7.
Analysis of surveillance data suggests enrichment of mammalian-adaptive vPol substitutions in IAVs isolated from magpies. a–e Abundance of mammalian-adaptive vPol sequences in H5, H7, and H9 IAVs isolated from the indicated species: a PB2-627K; b PB2-701N; c PB2-391Q; d PB2-456D; and e PA-100I. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals of the abundance of the specific substitution in the species population. Blue shading broadly highlights the range expected in species expressing only ANP32A_X1, thus indicating substitution abundances typically found in species selecting for avian-like vPol variants, while red shading broadly highlights the substitution abundance expected in species selecting for mammalian-like vPol variants. Stars indicate that the identified mammalian-like vPol substitutions are significantly higher in abundance than those found in species expressing only ANP32A_X1 (i.e. gull). Significance was determined by a one-sided proportion test (*0.01 < p < 0.05; **0.001 < p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). All other comparisons were non-significant. Source data, including sample sizes, for all panels are provided in the Source Data file