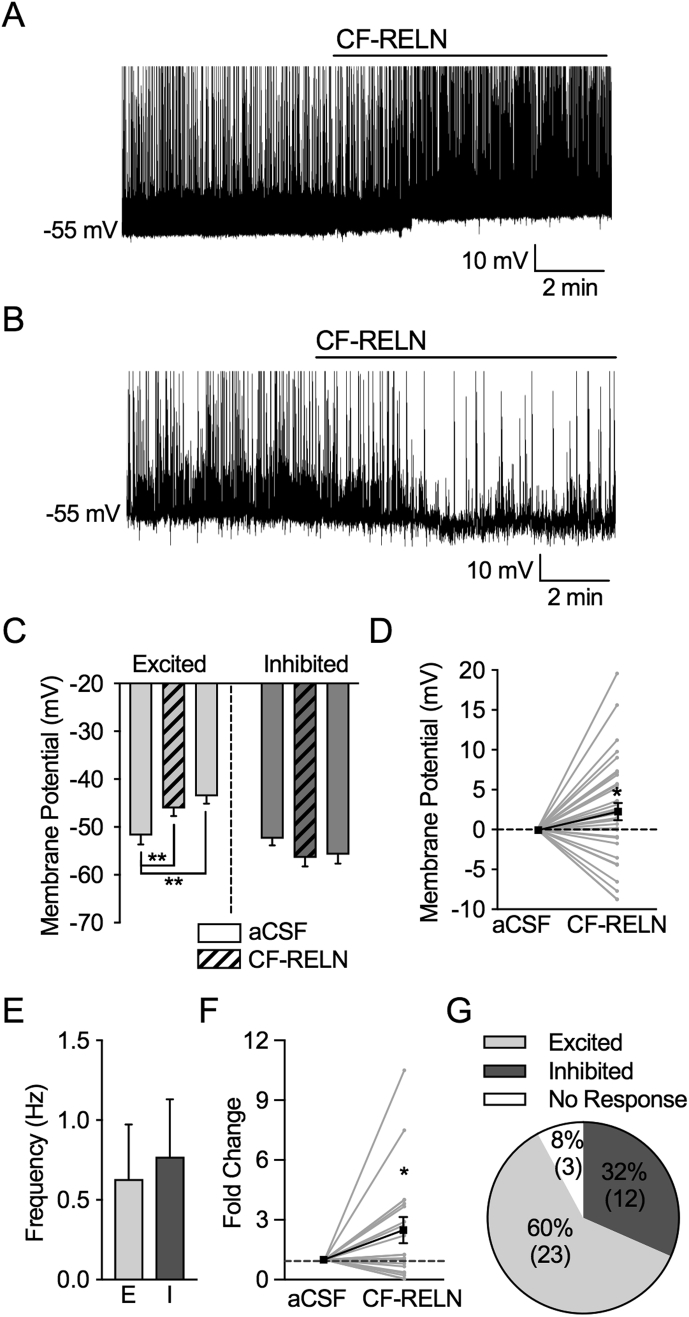
Figure 4.
CF-RELN has two distinct effects on action potential firing and membrane potential in ARH-POMC-EGFP neurons. A, B, Representative traces showing the firing rate and membrane potential before and after bath application of CF-RELN (100 nM) in a depolarized (A) and hyperpolarized (B) POMC-EGFP neuron. C, Mean membrane potential in CF-RELN excited (left; n = 23) and inhibited (right; n = 12) neurons (one-way ANOVA, Tukey's post-hoc) D, Change in membrane potential in all recorded neurons. E, Baseline action potential firing frequency of CF-RELN-excited (E) and inhibited (I) neurons. F, Normalized frequency of action potential firing from individual POMC-EGFP neurons before and after CF-RELN treatment (2.5 ± 0.7-fold; n = 20; One-way ANOVA with pairwise analysis; Bold line represents cumulative mean change; aCSF error bar represents pooled between-cell variance from all neurons). G, Ratio of CF-RELN in inhibited, excited, and non-responsive (n = 3) neurons as determined by Kolmogorov–Smirnov (KS) test. (Error bars indicate ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).