Figure 7.
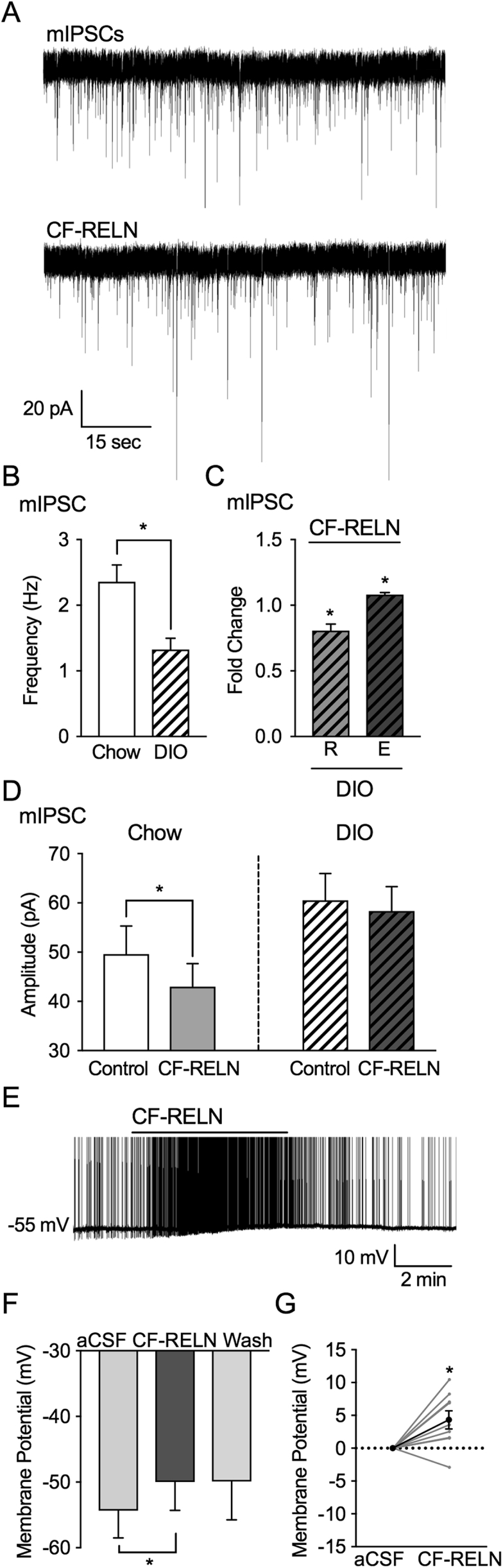
DIO alters actions of CF-RELN on mIPSC amplitude in ARH-POMC-EGFP neurons, but not membrane potential. A, Representative trace from a voltage-clamp experiment showing reduced mIPSC frequency after bath application of RELN (100 nM) in a POMC-EGFP neuron from DIO mice. B, Basal mIPSC frequency in POMC-EGFP neurons from chow fed (n = 14) and DIO mice (n = 15) C, Fold change of mIPSC frequency in neurons which CF-RELN reduced (R; 0.8 ± 0.0-fold; n = 7) or enhanced (E; 1.1 ± 0.1-fold; n = 8) mIPSC frequency as determined by KS-test D, Mean amplitude of mIPSCs in POMC-EGFP neurons from chow fed (n = 14) and DIO mice (n = 15) before and after RELN application. E, Representative current-clamp trace of showing membrane depolarization of a POMC-EGFP neuron in a DIO mouse after bath application of CF-RELN (100 nM). (F) Mean and change in (G) membrane potential before and after application of CF-RELN in DIO mice (n = 10). (Between-cell analysis using a Mixed-effects model with Tukey's post-hoc analysis *p < 0.05).
