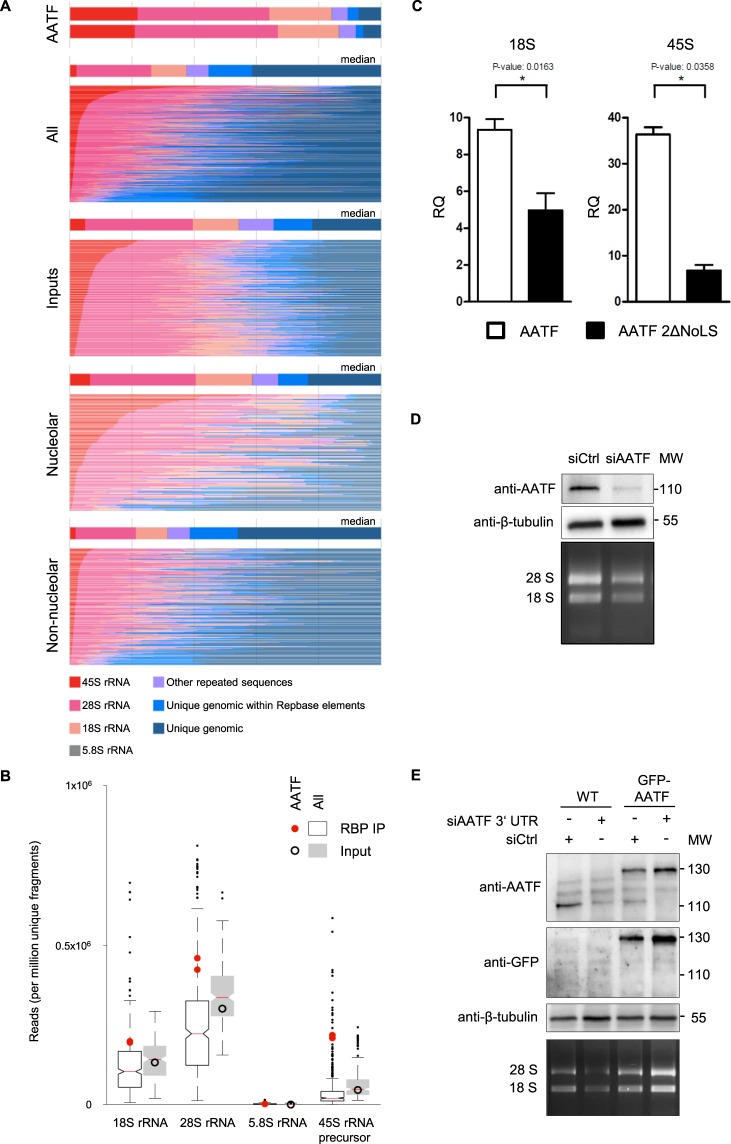
Figure 1.
Analysis of AATF-bound RNA biotypes identified by eCLIP. (A) Stacked bar colors indicate the fraction of reads mapping to indicated ribosomal RNA, other repeat elements, or uniquely to the human genome. For comparisons the total number of ENCODE datasets were used (223 datasets of 150 RBPs)58. All = all datasets, inputs = all input controls, nucleolar = all nucleolar RBPs among the ENCODE datasets, non-nucleolar = all non-nucleolar RBPs among the ENCODE datasets; “unique genomic within Repbase elements” = mapping uniquely to a repeat-masker identified element in the genome, “other repeated sequences” = mapping to the canonical repetitive elements in the family analysis. Nucleolar or non-nucleolar localization of RBPs was based on immunofluorescence data from the ENCODE consortium (see methods section for details). (B) Box plot comparison of AATF eCLIP-seq data to input and to 150 ENCODE RBPs showing enrichment of rRNA species in IP (red dot) over input (black circle) is specific for AATF. The other 150 ENCODE RBPs show a decrease of rRNA species in the IP (white box) compared to inputs (grey box). RNA species are plotted against the reads identified per million unique fragments. (C) RIP-qPCR analysis of 18S rRNA and 45S pre-rRNA transcripts validating the capacity of AATF to bind rRNA. Full-length FLAG-tagged AATF, the FLAG-tagged AATF 2ΔNoLS truncation or FLAG-tagged RFP (red fluorescent protein) were transiently overexpressed in HEK 293T cells and immunoprecipitated in RNA-interaction preserving conditions. Quantification of co-precipitated rRNA revealed a significant reduction of RNA binding for both ribosomal transcripts after loss of the two NoLS sites. RQ: relative quantification. CT values for WT AATF, 2ΔNoLS AATF and RFP were normalised against the corresponding input (delta CTIP-INPUT), and consecutively against RFP (delta delta CT, e.g. delta CTAATF − delta CTRFP). FLAG-RFP served as negative control. Experiments were carried out in three biological replicates, using two technical replicates each. Error bars depict the standard deviation. For western blot of IP from whole cell lysates showing equal protein amounts see Suppl. Fig. 1F. (D) Knockdown of AATF leads to a reduction of rRNA. The CDS of AATF was targeted with siRNA in mIMCD3 cells, which induced a significant depletion of endogenous AATF and was accompanied by a decrease in rRNA after 48 h of incubation. Top panel: western blot with anti-AATF antibody. Middle panel: anti-β-tubulin western blot (loading control). Bottom panel: EtBr stained agarose gel. MW: protein molecular weight marker (kDa). (E) Expression of AATF single-copy transgene rescues reduction of rRNA in AATF depleted U2OS cells. siRNA against the 3′UTR of AATF was transfected into wild-type U2OS cells and U2OS cells with a TALEN mediated, single-copy integration of GFP-AATF lacking the endogenous 3′UTR into the AAV locus. The 3′UTR specific knockdown of AATF in the wild type cells lead to a reduction of the 18S and 28S rRNA. The expression of the GFP-tagged transgene in the TALEN manufactured U2OS GFP::AATF cell line rescued the amount the rRNA species. Top panel: western blot with anti-AATF antibody. Middle panel: anti-β-tubulin western blot (loading control). Bottom panel: EtBr stained agarose gel. MW: protein molecular weight marker (kDa).