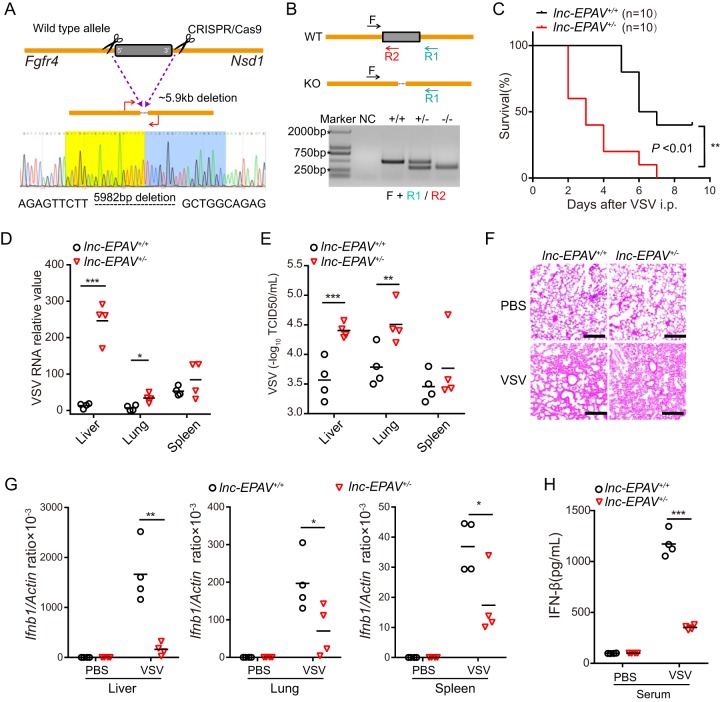
FIG 6.
lnc-EPAV protects mice against viral infection. (A) Schematic diagram of CRISPR/Cas9 knockout strategies at lnc-EPAV loci. A deletion of 5,982 bp was confirmed by Sanger sequencing. (B) Genotyping of lnc-EPAV knockout (KO) mice. Genomic DNA PCR products were derived from wild-type, monoallelic-deletion, or biallelic-deletion mice. NC, negative control. (C) Survival of 6-to-8-week-old lnc-EPAV+/+ or lnc-EPAV+/− mice (n = 10 mice per group) after intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of VSV (5 × 107 plaque forming units [PFU] per mouse). **, P < 0.01 (log rank test). (D and E) qPCR analysis of VSV RNA (D) and TCID50 assay of VSV particles (E) in the liver, lung, and spleen of lnc-EPAV+/+ and lnc-EPAV+/− mice infected with VSV (5 × 107 PFU per mouse) via intraperitoneal injection for 48 h. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (Student′s t test). (F) Hematoxylin-and-eosin staining of sections of lungs from mice processed as described for panel B. Bars, 50 μm. PBS, phosphate-buffered saline. (G) qPCR analysis of Ifnb1 expression in the liver (left panel), lung (center panel), and spleen (right panel) from mice as in B. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (Student′s t test). (H) IFN-β protein levels in serum from mice processed as described for panel B. ***, P < 0.001 (Student′s t test).