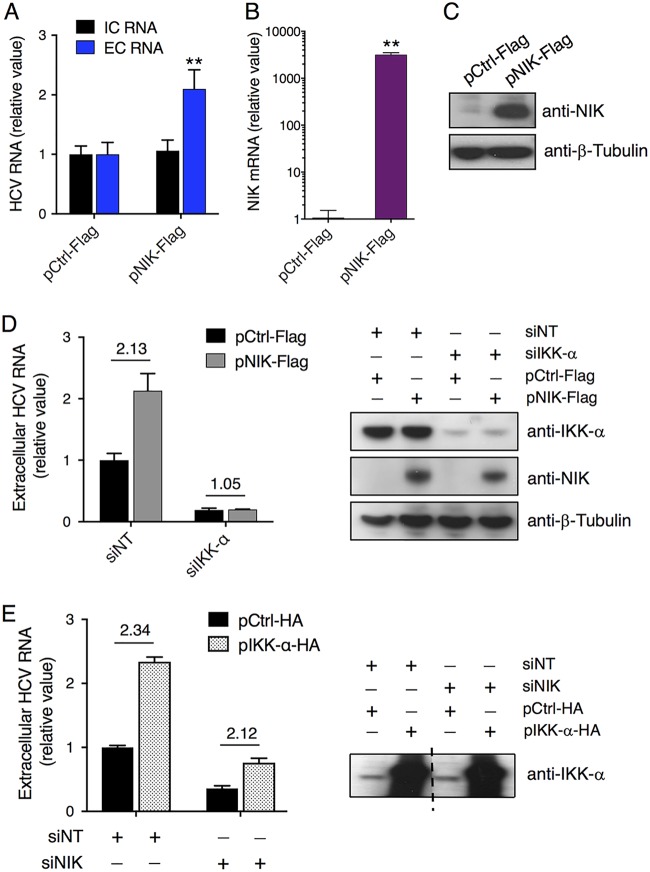
FIG 2.
NIK enhances HCV RNA production and secretion that are mediated by IKK-α. (A) Effect of NIK overexpression on intracellular and extracellular HCV RNA levels. (B and C) Transfection efficiency of Flag-tagged NIK plasmid in Huh7.5.1 cells, determined by measuring NIK mRNA levels through qPCR (B) or NIK protein levels by Western blotting (C). β-Tubulin was used as a loading control. (D and E) The proviral function of NIK acts upstream of the IKK-α signaling pathway. (D) Huh7.5.1 cells were treated with siNT or siIKK-α and then transfected with control (pCtrl-Flag) or NIK (pNIK-Flag) plasmid. The cells were subsequently infected with HCV. At 48 h postinfection, extracellular HCV RNA levels were measured by qPCR (left panel). Western blots (right panel) showed overexpression and knockdown efficiency of various plasmids or siRNAs used in the left panel. (E) Cells pretreated with NT or IKK-α siRNA were transfected with control (pCtrl-HA) or IKK-α (pIKK-α-HA) plasmid and then infected with HCV. After 48 h, extracellular HCV RNA levels were measured by qPCR (left panel). The right panel shows IKK-α overexpression efficiency by Western blotting. The middle of the same blot containing other lanes was removed, as indicated by a dashed line. (A, B, D, and E) Values are normalized as relative values to the negative-control siRNA and/or plasmid (as 1), and error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM) (n = 3). **, P < 0.01, determined by Student’s t test. NS, not significant. Triplicates were performed for each experimental condition in all cell culture experiments. All results are representative of three separate experiments.