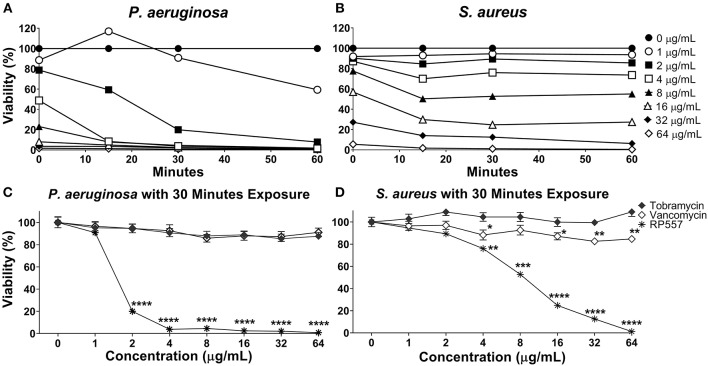
Figure 3.
RP557 immediately destroys P. aeruginosa and S. aureus in an increasing dose-dependent manner. The bactericidal effectiveness of RP557, tobramycin and vancomycin were evaluated against bioluminescent P. aeruginosa 19660 (A) and S. aureus 49525 (B) through 60 min of exposure. The concentration dependence of RP557, tobramycin and vancomycin following 30 min of exposure with P. aeruginosa and S. aureus is shown in (C,D), respectively. The bioluminescence of viable cells was quantitated non-invasively with an IVIS Lumina bioimaging system. Bioluminescence reflects bacterial viability as is directly correlated with number of colony forming units. Data represent the mean ± SE of triplicate replicates from two independent experiments; statistically significant (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001), using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey analysis. For some points, the error bars are shorter than the height of the symbols.