FIGURE 4.
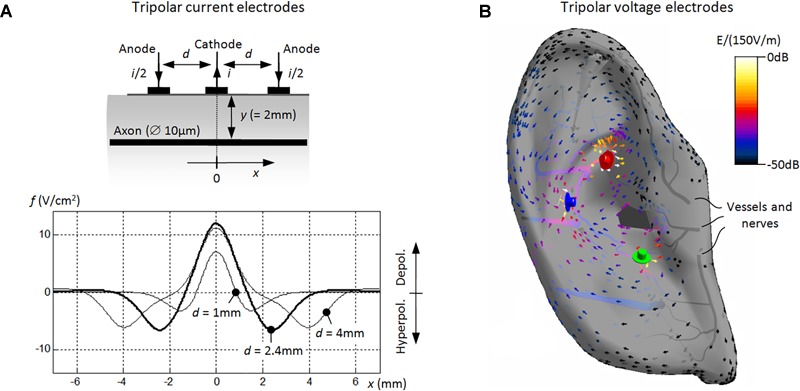
Numerical modeling of aVNS with three stimulation electrodes. (A) Basic model of the tripolar stimulation with surface current electrodes. A single cathode carries the current i (=1 mA) and the two surrounding anodes i/2 each. The unmyelinated axon lays in parallel to electrodes at the depth of 2 mm. Activating functions f(x) are shown along the axon’s coordinate x, showing the influence of the electrode separation d. With decreasing d, the depolarized segment of the axon narrows [i.e., Δx decreases for f(x) > 0] while the local depolarization strength decreases [i.e., f(x) decreases for f(x) > 0]. (B) Advanced model of the tripolar stimulation with needle voltage electrodes. The spatial distribution of the local electric field E (in dB related to 150 V/m) is shown within the outer ear with the electric potential 1 V for the red electrode, –1 V for the blue, and 0 V for the green. In fact, the gradient of the electric field [proportional to f(x)] determines the potential excitation of straight nerves along x aligned typically along auricular vessels (Figure 2).
