Figure 7.
Coelomocyte-Localized LIPL-5/LIPF Rescues Bacterial Deprivation-Induced Fat Catabolism and Lifespan Extension in lipl-5(ok3581) Mutants
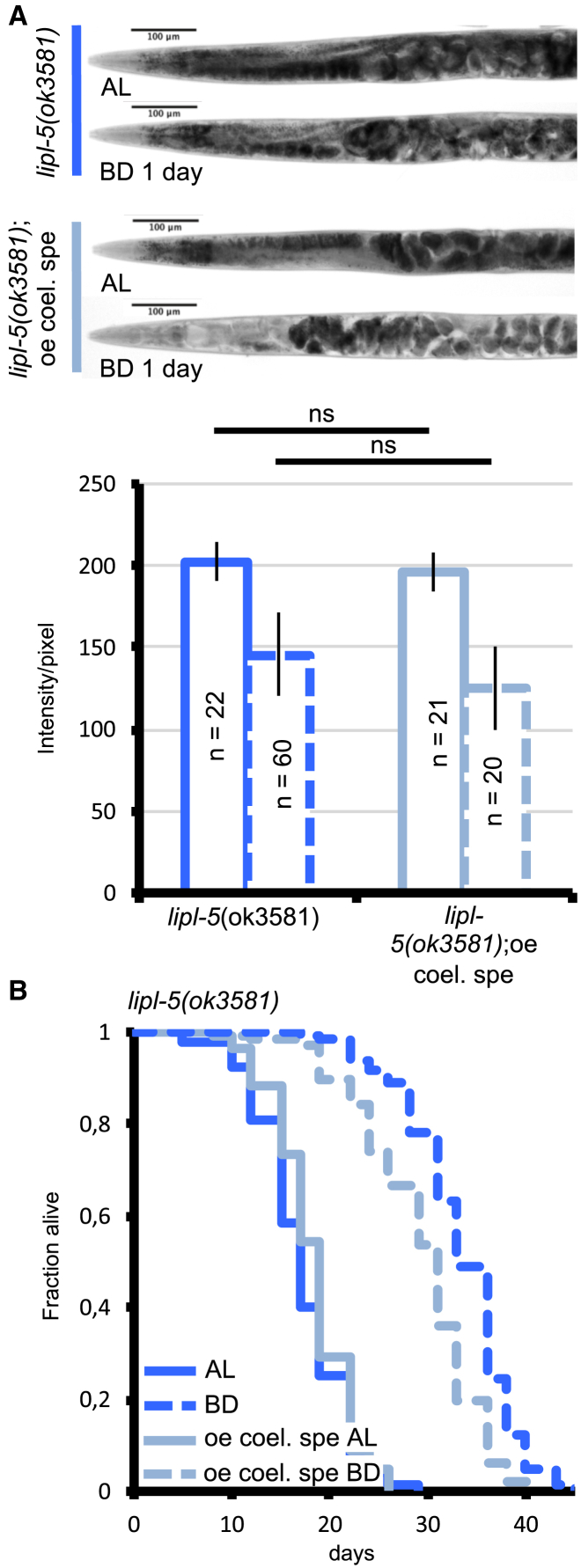
(A) Light micrographs of representative oil red O (ORO)-stained whole animals (upper panels) and densitometric quantification of staining of the two first intestinal cells after background removal (lower panels) for lipl-5(ok3581) mutants with or without coelomocyte-specific (cc1-driven) overexpression of lipl-5. Animals were fed ad libitum (AL) or subjected to bacterial deprivation (BD) for 1 day. Mean ± SD of n = at least 20 worms. ns, not significant; two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test. Representative of 3 biological replicates.
(B) Lifespan analyses of C. elegans fed AL or subjected to BD. BD extended lifespan by 83% for lipl-5(ok3581) mutants (p < 0.0001) and by 70% for lipl-5(ok3581) mutants overexpressing lipl-5 specifically in coelomocytes (p < 0.0001). These two strains exhibit similar lifespan in AL (p = 0.143), but in BD, lipl-5(ok3581) mutant animals had a lifespan 12% longer when compared with lipl-5(ok3581) mutants overexpressing lipl-5 specifically in coelomocytes (p < 0.001). Mantel-Cox log-rank test (see Table S2 for number of replicates).