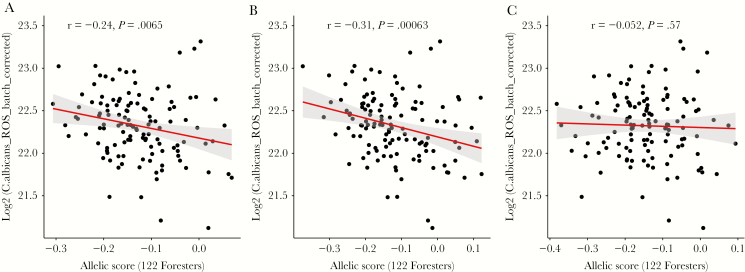
Figure 4.
Candidemia-associated loci have a functional role in anti-Candida defense mechanism by influencing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in response to Candida albicans. Scatterplots of significant correlations between ROS production and allelic scores constructed as the total number of risk alleles from (A) 24 susceptibility variants that influence cytokines and (B) 16 variants that only influence monocyte-derived cytokines (interleukin [IL]-6, IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor α) in response to either C albicans yeast or hyphae in either of the 3 cell systems (peripheral blood mononuclear cells, whole blood, and monocyte-derived cytokines). (C) Scatterplot of nonsignificant correlation between ROS production and allelic scores constructed as the total number of risk alleles from 12 susceptibility variants that only influence T-cell cytokines (IL-17, IL-22, and IFNγ) in response to either C albicans yeast or hyphae in either of the 3 cell systems. Allelic scores were weighted by odds ratio. Genotype and ROS production data were available for 122 individuals from the 200FG cohort. The (rank-based) Spearman correlation was calculated between ROS production and allelic scores. P < .05 was considered as the threshold for significance.