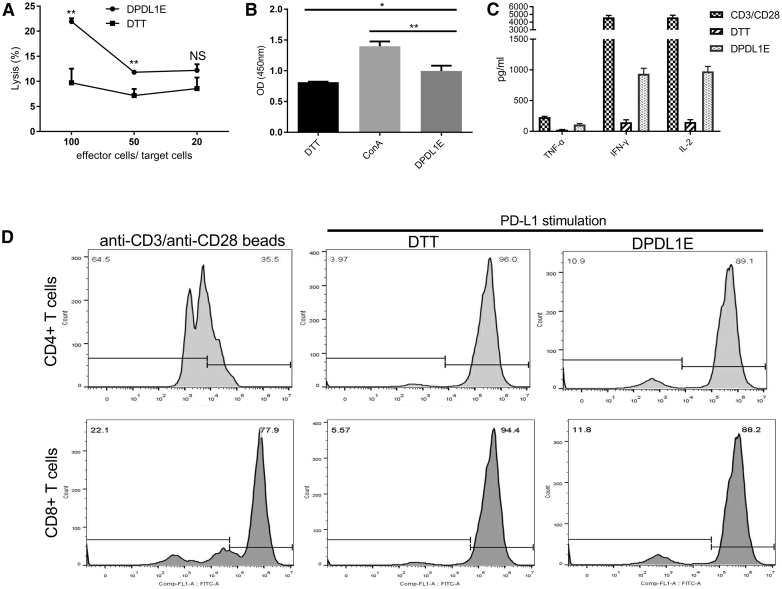
Figure 3.
The CTL Response Induced by DPDL1E Vaccination
(A) Lymphocytes from spleens of DPDL1E- and DTT-immunized mice were used as effector cells. PD-L1-positive expressed B16-F10 cells were used as target cells. Cytotoxicity was assessed with an LDH release assay. Statistically significant differences were determined using Student’s t test. (B) Lymphocytes isolated from DTT- and DPDL1E-immunized mice were stimulated with His-PD-L1 recombinant protein or Con A for 72 h. Cell proliferation was measured with the CCK-8 method. (C) The concentrations of TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-2 in supernatant after 72 h stimulation. The cytokines were detected using an ELISA kit. Anti-CD3/CD28 beads (0.5 μg/mL) were used as a positive control. (D) Proliferation of T cells was determined using a CFSE-based assay in vitro. CD8+ and CD4+ T cells were gated and analyzed using FCM. Both CD8+ and CD4+ T cells proliferated more than the DTT control group after His-PD-L1 stimulation. Statistically significant differences were calculated by Student’s t test. NS, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.