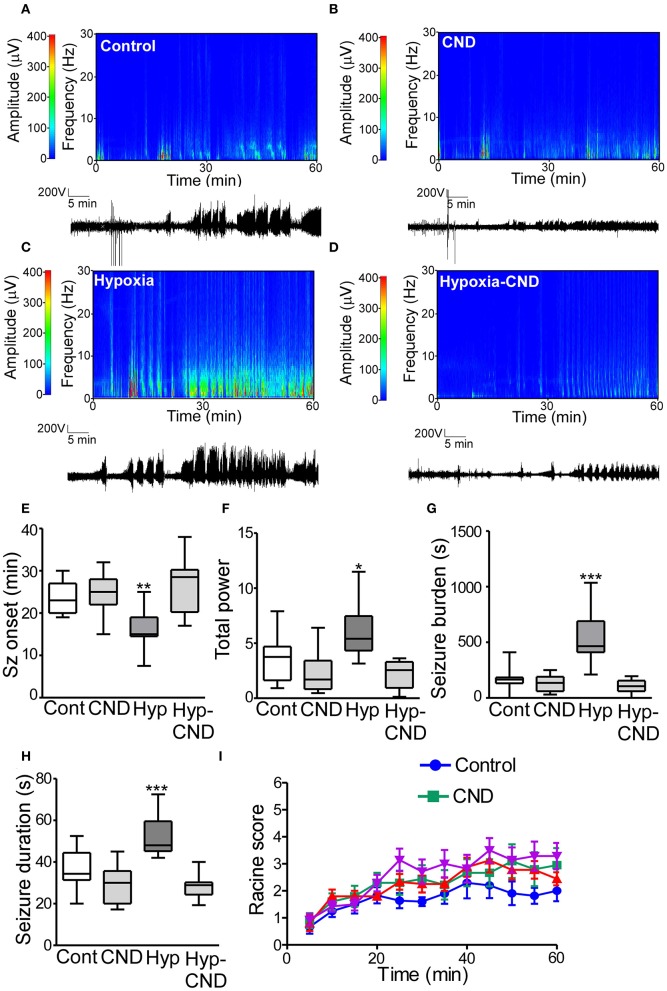
Figure 7.
CND improves the susceptibility to develop seizures later in life after hypoxia-induced seizures in a neonatal mouse model. Five weeks after neonatal treatment, mice were implanted with electrodes and challenged with systemic KA (15 mg.kg−1), EEG and behavior were recorded. (A–D) Representative spectrograms and corresponding EEG traces from the control (A), CND (B), Hypoxia (C), and hypoxia-CND group (D). (E–H) Quantification of seizure onset, total power, total seizure burden, and seizure duration during the 60 min of recording. (E) Seizure onset was earlier in the hypoxia group compared to the control, CND and Hyp-CND group (n = 11–13, **p < 0.01 compared to control, CND and Hyp-CND group. F: 11.41, t: 3.896 (vs. control), t: 4.247 (vs. CND), t: 5.387 (vs. Hyp-CND)]. (F) Total power was higher in the hypoxia group compared to the control, CND and Hyp-CND group [n = 11–13, *p < 0.05 compared to control, CND and Hyp-CND group. F: 10.85, t: 3.183 (vs. control), t: 4.713 (vs. CND), t: 5.051 (vs. Hyp-CND)]. (G) Similar results were found in seizure burden in the hypoxia group [n = 11–13, ***p < 0.001 compared to control, CND and Hyp-CND group. F: 25.89, t: 6.514 (vs. control), t: 7.038 (vs. CND), t: 7.585 (vs. Hyp-CND)]. (H) Hypoxia-exposed pups developed on average longer seizures [n = 11–13, ***p < 0.001 compared to control, CND and Hyp-CND group. F: 18.000, t: 4.555 (vs. control), t: 6.050 (vs. CND), t: 6.381 (vs. Hyp-CND)]. (I) Seizure behavioral score taken every 5 min over the 60 min period using the modified Racine scale for mice (n = 11–13).