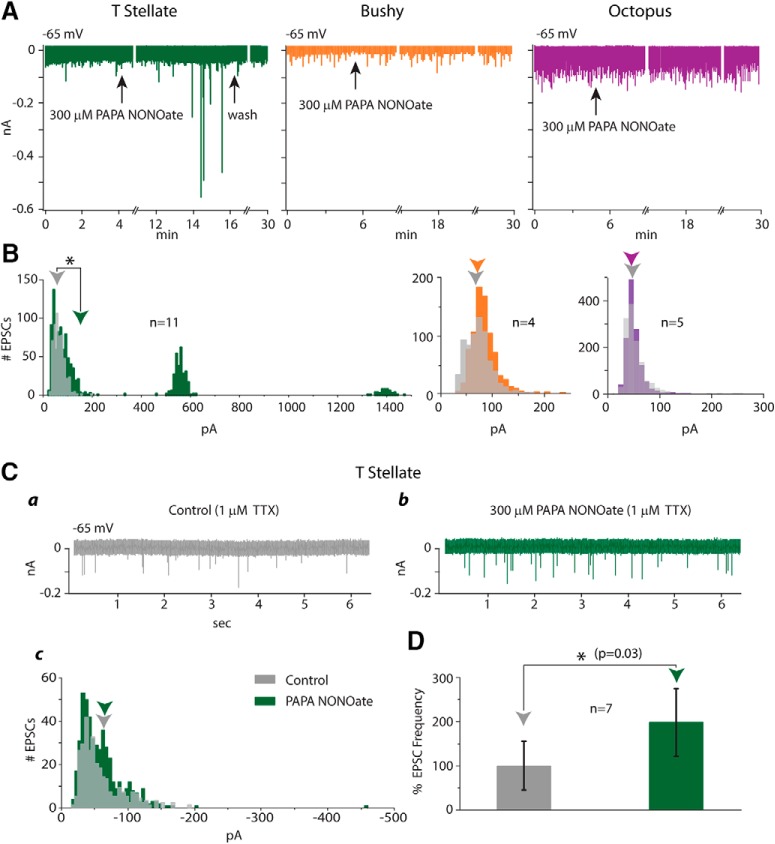
Figure 4.
Comparison of action of the NO donor, PAPA NONOate, on T-stellate cells with its action on the other groups of principal cells of the VCN, bushy and octopus cells. Asterisk denotes a significant difference with p < 0.05. A, Recordings of EPSCs in a T-stellate cell (green), a bushy cell (orange), and an octopus cell (purple) show that PAPA NONOate evoked large EPSCs, not of uniform amplitude, in the T-stellate cell, but not in the bushy or octopus cell. B, Histograms of amplitudes of EPSCs recorded from n cells in each group show that PAPA NONOate caused no change in the mean amplitude of EPSCs in bushy cells (p = 0.5) or octopus cells (p = 0.9). In the presence of PAPA NONOate, spontaneous EPSCs in T-stellate cells were on average significantly larger than under control conditions (p = 0.015). C, In the presence of TTX, PAPA NONOate increased the frequency, but not the amplitude, of EPSCs. Ca, T-stellate cell had spontaneous mEPSCs in the presence of TTX. Cb, In the continued presence of TTX, PAPA NONOate evoked more rapid EPSCs. Cc, The amplitude distribution of EPSCs was not significantly different in the presence and absence of PAPA NONOate (p = 0.93). D, The increase in EPSC frequency caused by the application of PAPA NONOate in 7 cells was significant.