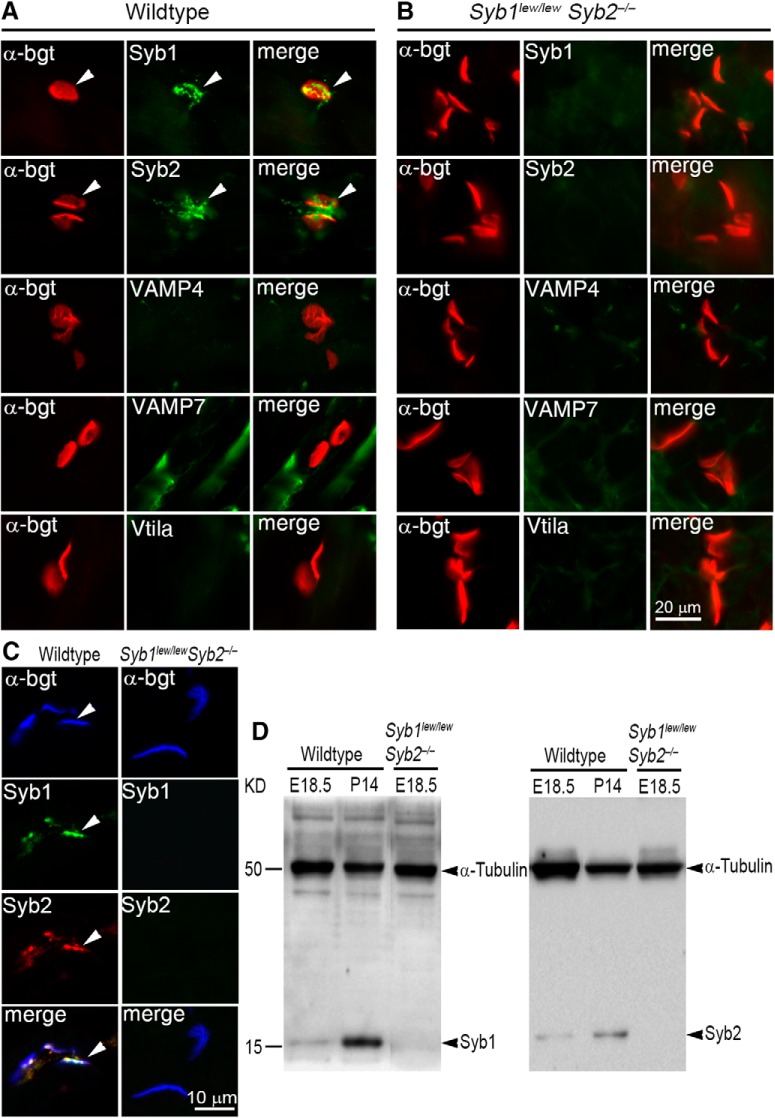
Figure 1.
Synaptobrevin vSNAREs (Syb1 and Syb2) are coexpressed at developing motor nerve terminals and spinal cords. A, B, Frozen section of embryonic diaphragm muscles (E18.5) from WT (A) and Syb1lew/lewSyb2−/− mice (B), doubly labeled with Texas red-conjugated α-bgt for postsynaptic AChRs (red, arrowhead) and specific antibodies against a SNARE protein (green): Syb1 (VAMP1), Syb2 (VAMP2), VAMP4, VAMP7, or Vti1a. Both Syb1 and Syb2 are detected at the NMJ in the WT (A) but not in Syb1lew/lewSyb2−/− mice (B). No detectable level of VAMP4, VAMP7, or Vti1a was found at the NMJ in WT or Syb1lew/lewSyb2−/− mice. C, Diaphragm muscle sections (E18.5) were triply labeled with AlexaFluor-647-conjugated α-bgt, anti-Syb1(rabbit polyclonal, green), and anti-Syb2 (mouse monoclonal, red) antibodies. Merged image shows that Syb1 and Syb2 are coexpressed at the NMJ in the WT (C, left panels) but absent in Syb1lew/lewSyb2−/− mice (C, right panels). D, Western blot analyses of spinal cord homogenates at E18.5 (WT and Syb1lew/lewSyb2−/−) and P14 (WT). Syb1 expression is markedly increased at P14, compared with that at E18.5. Scale bars: A, B, 20 μm; C, 10 μm.