Figure 1.
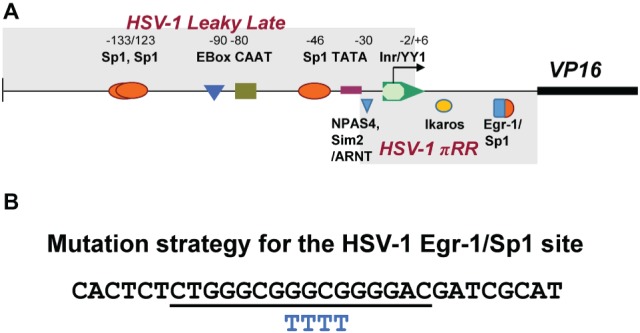
Schematic representation of transcription factor (TF)-binding sites in HSV-1 VP16 promoter. (A) Shown above the line are the names of TF-binding sites identified as important for VP16 promoter strength Wagner and colleagues in transient assays (Lieu and Wagner, 2000). Below the line are high-scoring TF sites identified as potentially important for de novo VP16 expression (boxed and labeled as HSV-1πRR) that were simultaneously mutated resulting in failure to initiate lytic gene expression in sensory neurons in vivo (Sawtell and Thompson, 2016a,b). (B) Shown is the sequence of a 30mer oligonucleotide that contains a canonical overlapping Egr-1/Sp1 site (underlined) in the HSV-1 VP16 gene 5′UTR. Below this are shown the four bases that were changed to “T” residues to mutate the TF sites (BP 105,134–105,137).
