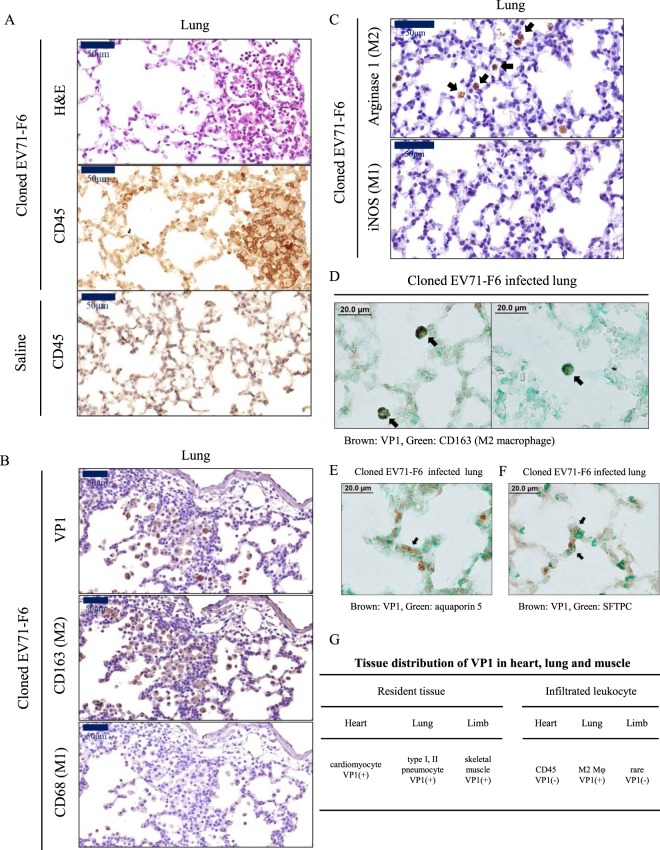
Figure 5.
VP1-positive infiltrating M2 macrophage and VP1-positive pneumocytes were detectable in the orally infected lung. Orally infected mice were sacrificed on day 16 post-infection (Fig. 1B). Adjacent lung sections were examined with (A) H&E and IHC staining for a pan-leukocyte marker CD45. Massive leukocyte infiltration was detected. (B) VP1 and CD163 (M2 macrophage), but not CD68 (M1 macrophage), were detected by IHC in adjacent lung sections. (C) Similarly, arginase 1 marker for M2 macrophages, but not iNOS marker for M1 macrophage, was visualized in the alveoli by IHC staining. (D) VP1-positive (brown) M2 macrophages (CD163, green) were observed in both panels by IHC double staining. (E,F) VP1-positive signal was detected in both type I (aquaporin 5) and type II pneumocytes (surfactant protein C). (G) Distribution of VP1 in heart, lung and muscle, as well as their respective infiltrating leukocytes.