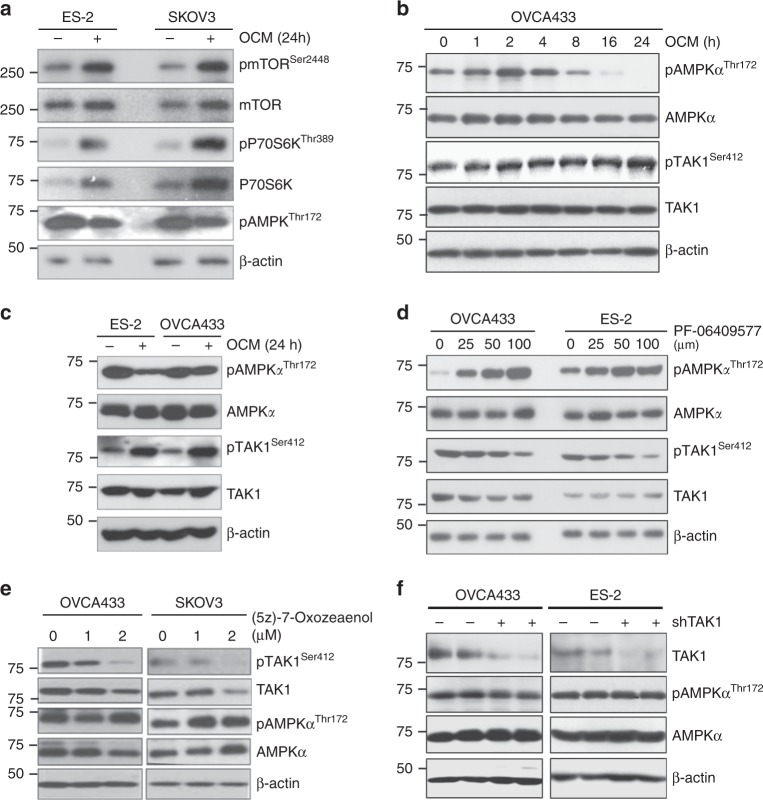
Fig. 5.
Oncogenic pathways regulated by AMPK in ovarian cancer cells. a Long-term culture with OCM (24 h) leads to reduction in AMPK activity (pAMPKThr172), activation of mTOR activity (pmTORSer2448), and increased phosphorylation of p70S6K (pP70S6KThr389) in ES-2 and SKOV3 cells. b While culturing OVCA433 cells in OCM for 24 h leads to downregulation of pAMPKThr172, but elevation of the level of pTAKSer412. c Long-term culture with OCM (24 h) with ES-2 and OVCA433 causes an inverse relationship between the AMPK (reduced pAMPK Thr172) and TAK1 (increased pTAK1Ser412) activities. d The level of pAMPKThr172 is increased, while the level of pTAK1Ser412 is reduced upon treatment with AMPK activator, PF-06409577 (24 h), in a dose-dependent manner in OVCA433 and ES-2 ovarian cancer cells. e Co-treatment with TAK1 inhibitor, (5Z)-7-Oxozeaenol (2.5 μM), substantially inhibits the expression of pTAK1Ser412 in a dose-dependent manner (24 h), and this effect is accompanied by an increase in pAMPKThr172 levels in OVCA433 and SKOV3 cells. f Knockdown of endogenous TAK1 by shRNAi more than 70% does not alter either pAMPKThr172 or total AMPK in OVCA433 cells