Fig. 3.
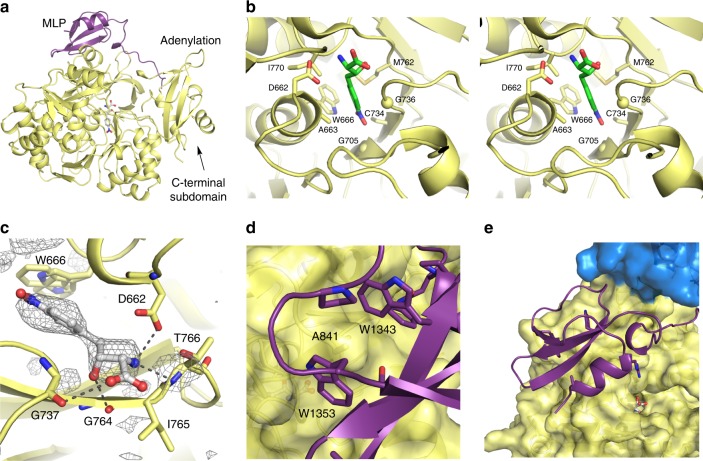
ObiF1 Adenylation domain structure and MLP interaction. a The MLP domain (purple) interacts with the A domain (yellow) in the adenylate-forming conformation. b Stereorepresentation of the specificity determining residues of the substrate binding pocket of the adenylation domain. Cα positions of two glycine residues are indicated with a sphere. Only a single conformation of the side chain of Trp666 is shown. c β-OH-p-NO2-homoPhe binds in the A domain active site where the β-hydroxyl forms H-bonds with backbone amide carbonyls of Gly737 and Gly764. Electron density (contoured at 2.5σ) calculated with mFo–DFc coefficients from an omit map (ligand occupancy set at zero) generated with simulated annealing. The α-amino group forms a salt-bridging interaction with Asp662 and an H-bond with the amide proton of Thr766. The side chain of Trp666, which adopts two alternate conformations, contributes to the hydrophobic pocket around the p-NO2-phenyl ring. d Trp1343 and Trp1353 of the MLP domain form a pocket around Ala841 of the A domain. e The MLP domain in relation to the C domain (blue) and A domain active site