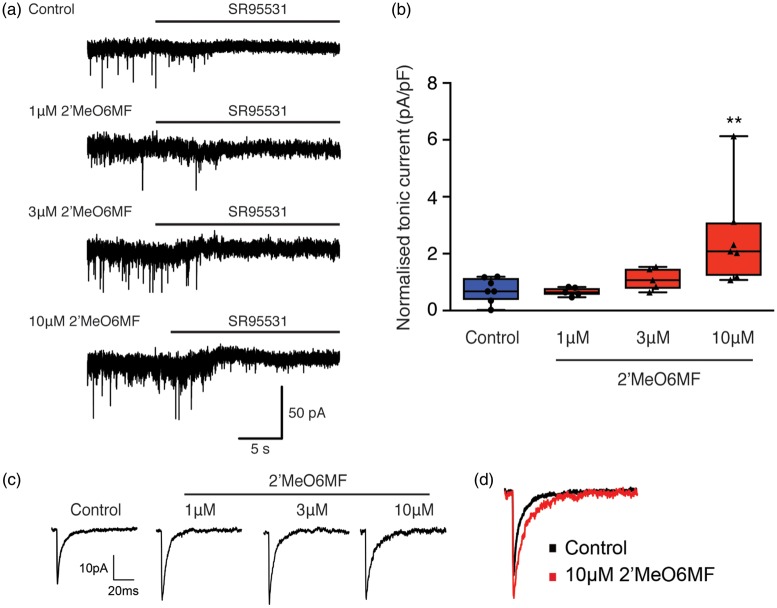
Figure 2.
2′MeO6MF acts on δ-containing GABAARs and increases tonic GABAAR currents in DGGCs. The effect of 2′MeO6MF on GABAAR-mediated inhibitory currents was assessed using DGGCs. Panel (a) shows representative holding current traces across time that were used to estimate the tonic currents from control and 2′MeO6MF-treated (1–10 µM) granule cells. 2′MeO6MF alone induces a small increase in tonic inhibition in granule cells. Horizontal bars indicate the application of the GABAAR antagonist SR95531 (>100 µM). 2′MeO6MF (1 and 3 µM) induced little or no increase in tonic current, while 10 µM 2′MeO6MF was able to induce a clear increase in tonic current in granule cells. Panel (b) box plot (whiskers: minimum and maximum; lines: median) showing the average (mean ± SD) GABAAR-mediated current density in granule cells in control (n = 7) and after application of 1 µM (n = 5), 3 µM (n = 5) or 10 µM (n = 7) 2′MeO6MF. Panel (c) and (d) show that 2′MeO6MF enhances phasic inhibition by increasing mIPSC amplitude at all three doses tested (1–10 µM). Panel (c) shows representative average mIPSC (n > 50 traces) in control conditions and after application of 2′MeO6MF (1–10 µM). Panel (d) shows an overlay of both the control mIPSC trace (black) and the 10 µM 2′MeO6MF mIPSC trace (red), highlighting the increase in amplitude upon application of 2′MeO6MF. **=P < 0.05, compared to the control tonic current. 2′MeO6MF: 2′-methoxy-6-methylflavone.