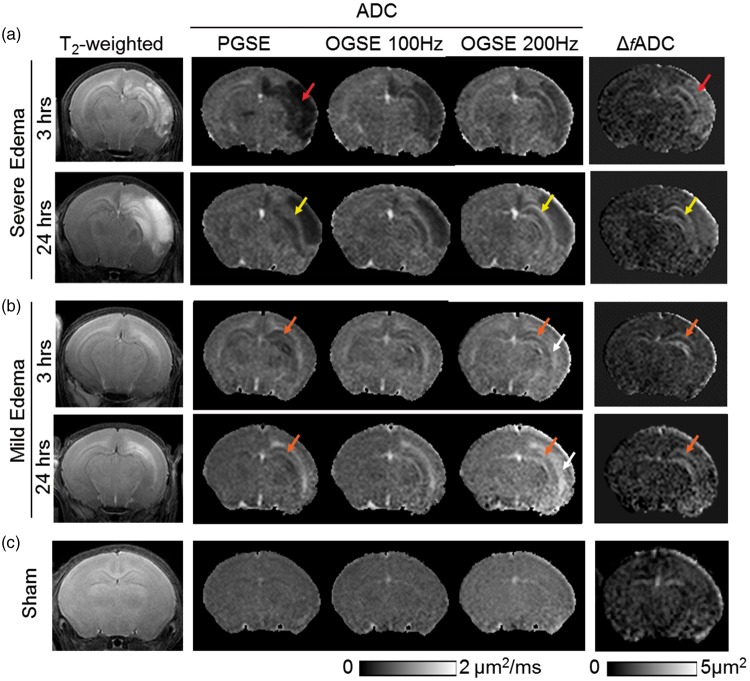
Figure 1.
MR images of neonatal mouse brains with severe (a) and mild (b) edema as well as images of sham controls (c) at acute (3–6 h) and sub-acute (24 h) stages post-injury. At 3–6 h, axial T2-weighted images show widespread hemispheric infarct (red arrows) in the severe edema case, and more localized edema (orange arrows) in the external capsule (EC) and hippocampus in the mild edema case. In the severe edema case, pseudo-normalization of PGSE-ADC signals (from 3 to 6 h to 24 h) can be found in the hippocampal CA1 region (indicated by the yellow arrows), whereas the OGSE-ADC (at 100 and 200 Hz) and ΔfADC images consistently highlight the damaged CA1 hippocampus. In the mild edema cases, early signal abnormality in CA1 hippocampus (orange arrows) was evident as early as 3 h after HI from OGSE-ADC at 200 Hz and Δf ADC maps. Hyperintense ADC signals in the CA1 hippocampus and EC (white arrows) are more pronounced in the OGSE-ADC maps than the PGSE-ADC maps at 24 h post-injury.