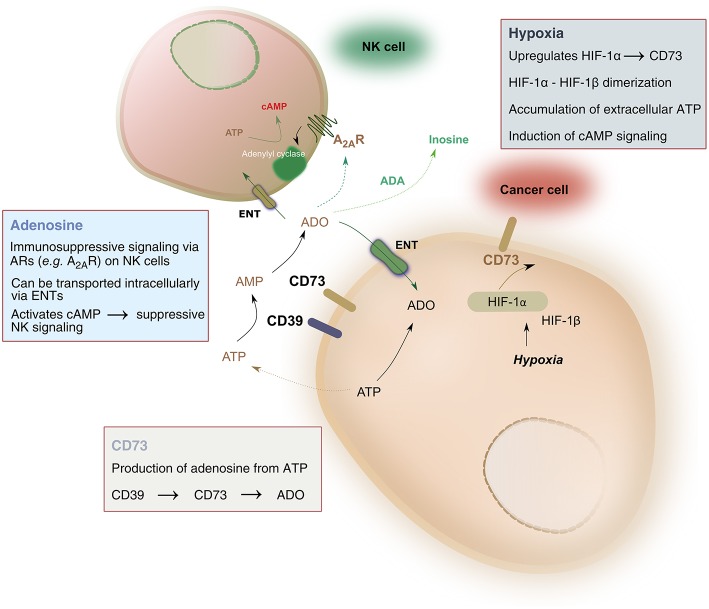
Figure 1.
Hypoxia-CD73 signaling on NK cells. Hypoxia induces the expression of CD73 via HIF-1, itself consisting of HIF1-α and HIF-1β. HIF-1, in turn, regulates immune responses to hypoxia by controlling glycolytic metabolism and NK cells' adaptation to low oxygen. CD73 dephosphorylates AMP, produced by the conversion of ATP to AMP catalyzed by CD39, to generate adenosine. Extracellular adenosine can be transported intracellularly via equilibrative nucleoside transporters (ENT) or it can signal via adenosine receptors on the surface on NK cells, most notably the A2A receptor (A2AR). A2AR signaling via adenosine was shown to result in dysfunction of NK cell metabolic and effector functions. Extracellular adenosine can also be converted to inosine via the catalytic activity of adenosine deaminase (ADA).