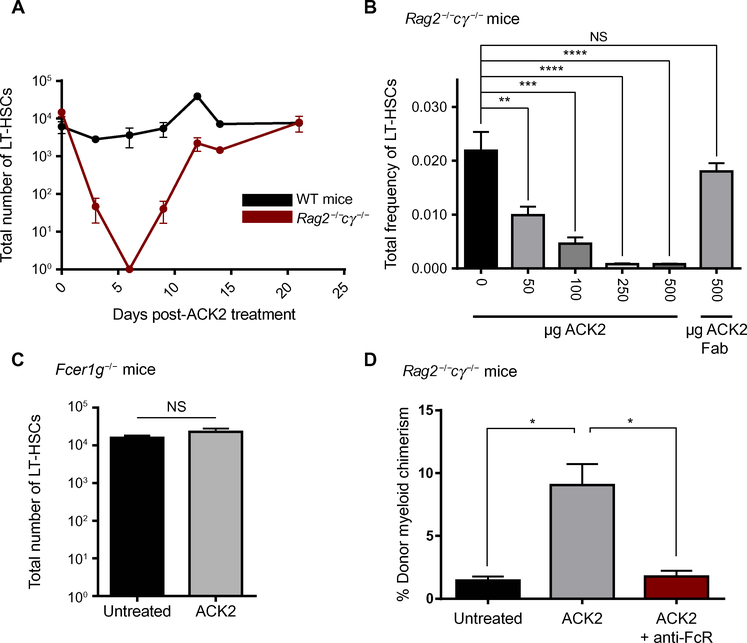
Fig. 1. Depletion of HSCs by anti–c-Kit antibody ACK2 is dependent on FcR activity.
(A) Total number of phenotypic Lin−c-Kit+Sca-1+CD150+Flt3−CD34− LT-HSCs in wild-type (WT) mice as compared to immunocompromised Rag2−/−cγ−/− mice after treatment with anti–c-Kit antibody ACK2 (n = 3 to 5 per group; experiment was repeated three times). (B) Total frequency of Lin−c-Kit+Sca-1+CD150+Flt3−CD34− LT-HSCs in Rag2−/−cγ−/− mice 6 days after treatment with increasing concentrations of ACK2 compared to 500 μg of ACK2 Fab (n = 3 per group). (C) Number of Lin−c-Kit+Sca-1+CD150+Flt3−CD34− LT-HSCs in Fcer1g−/− mice 6 days after ACK2 treatment as compared to untreated controls (n = 3; experiment was replicated in triplicate with similar results each time). (D) Frequency of donor-derived Mac-1+Gr-1+ granulocytes in peripheral blood of Rag2−/−cγ−/− animals after either ACK2 treatment or FcR blocking before ACK2 as compared to untreated recipients. Data and error bars in (B) to (D) represent means ± SEM. NS, not significant; ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.0005, **P < 0.005, *P < 0.05.