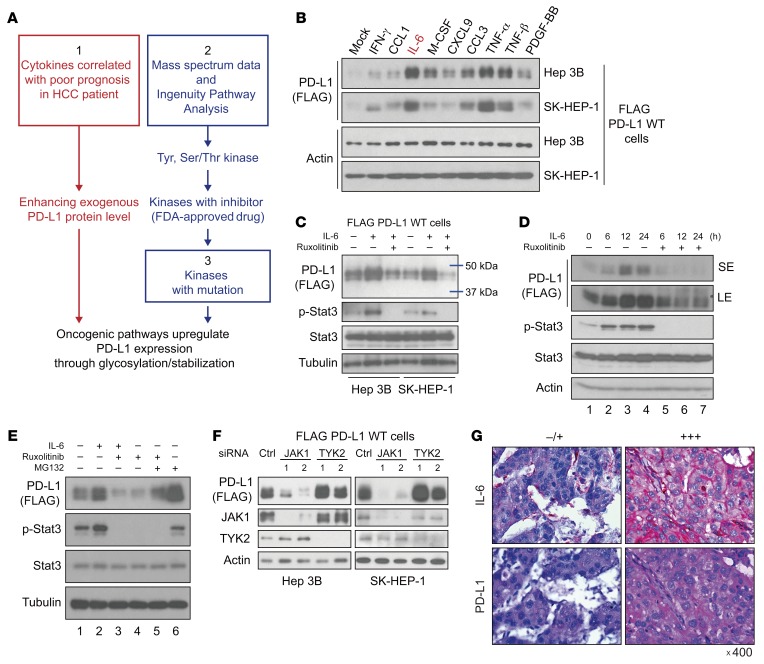
Figure 1. The IL-6/JAK1 pathway positively regulates PD-L1 protein stability, and IL-6 and PD-L1 expression is positively correlated in tumor tissues from HCC patients.
(A) Schematic of the strategy using the indicated criteria (1, 2, and 3) to identify pathways that potentially upregulate PD-L1 expression via posttranslational modifications. (B) Western blot (WB) analysis of exogenous PD-L1 expression in FLAG–PD-L1 WT–Hep 3B and WT–SK-HEP-1 cells stimulated with different cytokines for 18 hours. (C) WB analysis of exogenous PD-L1 expression in FLAG–PD-L1 WT–Hep 3B and WT–SK-HEP-1 cells under IL-6 stimulation (20 ng/mL) or cotreatment with the JAK1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib (10 μmol/L) for 18 hours. (D) WB analysis of exogenous PD-L1 expression in FLAG–PD-L1 WT–Hep 3B cells with IL-6 stimulation (20 ng/mL) or cotreatment with ruxolitinib (10 μmol/L) for the indicated times. SE, short exposure; LE, long exposure. (E) WB analysis of exogenous PD-L1 expression in the presence or absence of IL-6 stimulation (20 ng/mL, 18 hours), ruxolitinib (10 μmol/L, 18 hours), or the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (10 μmol/L, 6 hours). (F) WB analysis of exogenous PD-L1 expression in FLAG–PD-L1 WT–SK-HEP-1 and WT–Hep 3B cells with knockdown of the indicated genes by siRNA. (G) Representative images of IL-6 and PD-L1 expression levels in tumor regions in HCC patients. Original magnification, ×400.