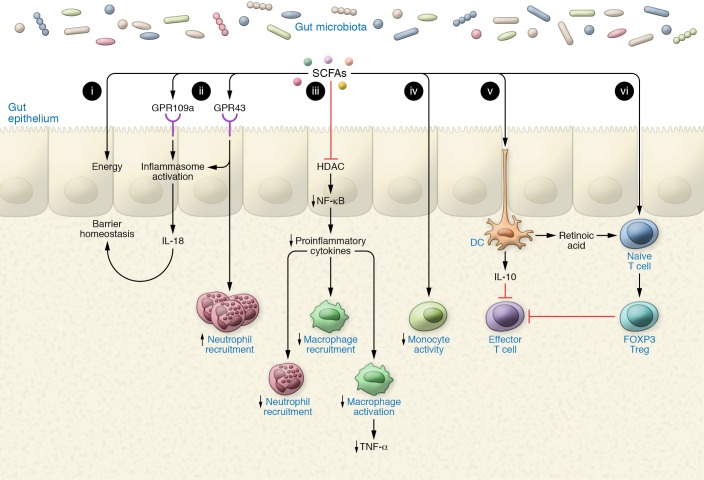
Figure 1. SCFAs bolster the gut epithelium and coerce a tolerogenic immune environment.
(i) SCFAs act as a major and preferred energy source to the colonic epithelium. (ii) SCFAs signal via GPR43/109a to induce inflammasome activation, culminating in IL-18 secretion, which functions in gut barrier homeostasis. (iii) SCFAs dampen NF-κB signaling via HDAC inhibition, thereby inhibiting secretion of proinflammatory cytokines. (iv) SCFAs inhibit recruitment and activation of macrophages and neutrophils through a reduction in proinflammatory cytokine production. (v) SCFAs induce a tolerogenic dendritic cell phenotype by inducing the secretion of IL-10 and retinoic acid. IL-10 inhibits effector T cell function, while retinoic acid binds to the retinoic acid receptor in naive T cells to induce their differentiation into Tregs. (vi) SCFAs induce Treg differentiation through HDAC inhibition, which inhibits the activity of effector T cells, thus establishing a tolerogenic immune environment.