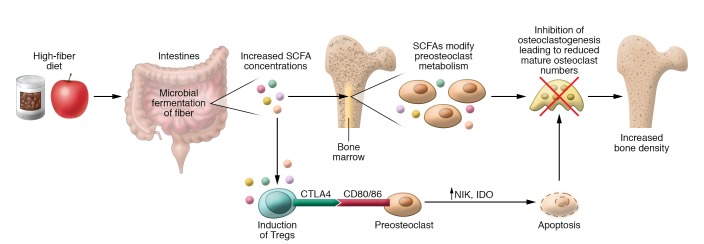
Figure 2. Direct and indirect effects of SCFAs on bone resorption.
SCFAs, the main metabolites derived from microbial fermentation of dietary fibers in the intestine, affect bone homeostasis via two routes. In addition to butyrate’s strong HDAC-inhibiting effects on osteoclasts, it directly induces metabolic reprogramming of osteoclast precursors, resulting in enhanced glycolysis at the expense of oxidative phosphorylation, thereby downregulating essential osteoclast genes such as TRAF6 and NFATc1. Indirect effects of SCFAs may account for their Treg-inducing capacity: Tregs were shown to suppress osteoclast differentiation via their secretion of antiosteoclastic cytokines as well as via a direct cell-cell contact–dependent, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase–inducing (IDO-inducing) mechanism. In summary, these data identify SCFAs as potent regulators of osteoclast metabolism and bone homeostasis.