Figure 2. CO binding to BvHbs by stopped-flow rapid mixing.
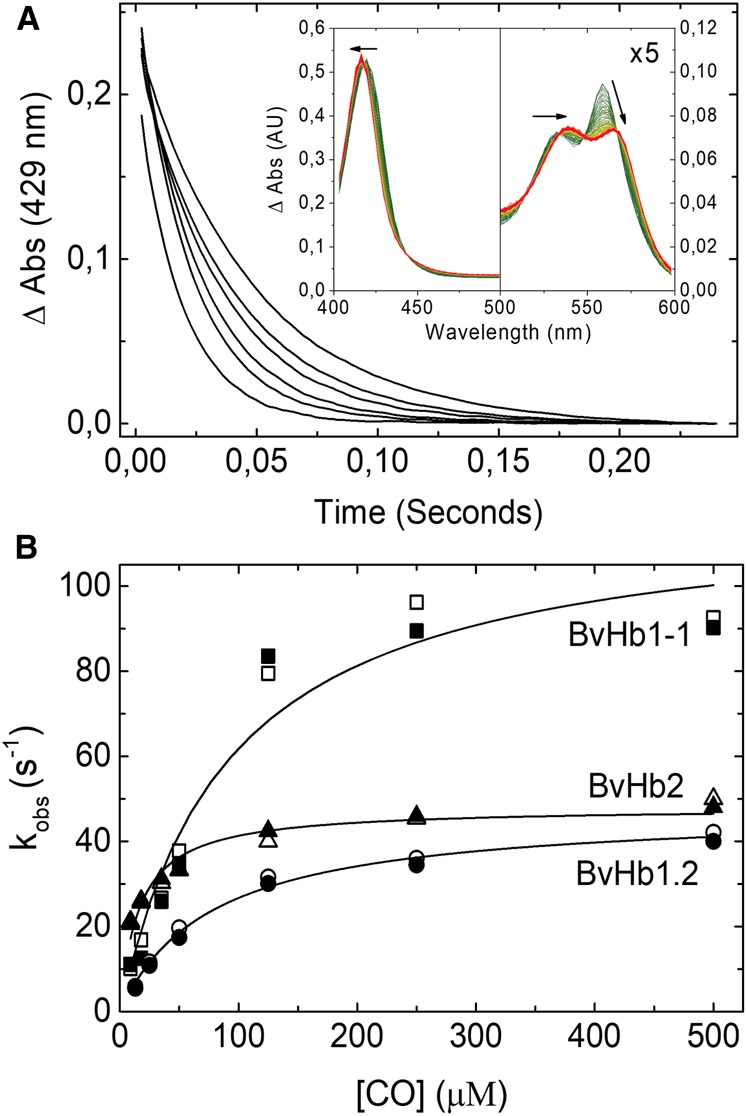
(A) Time courses for CO binding to BvHb2 following rapid mixing at different CO concentrations (from left to right: 500, 250, 125, 35, 18, and 9 µM) monitored at 429 nm. Inset, Absorbance spectra associated with the binding of CO to ferrous BvHb2. The direction of the spectra changes from deoxyHb (green) to HbCO (red). (B) CO dependance of the rate constants for binding to the three BvHbs determined by stopped-flow rapid mixing. The data are fitted to eqn 1 to extract the hexacoordination rates, kH and k-H. The closed and open symbols are kobs values monitored at 430 and 555 nm for BvHb1.1, 430 and 560 nm for BvHb1.2, and 429 and 558 nm for BvHb2.
