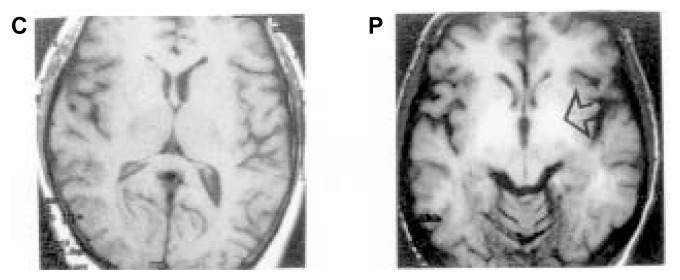
Figure 3.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of a healthy control subject (C) and an alcoholic cirrhotic patient of the same age (P). In the alcoholic patient, abnormally intense signals (arrow) are detected on both sides of the brain in a region called the globus pallidus. This phenomenon has been attributed to deposits of manganese in this brain area.
SOURCE: Lockwood et al. 1997.