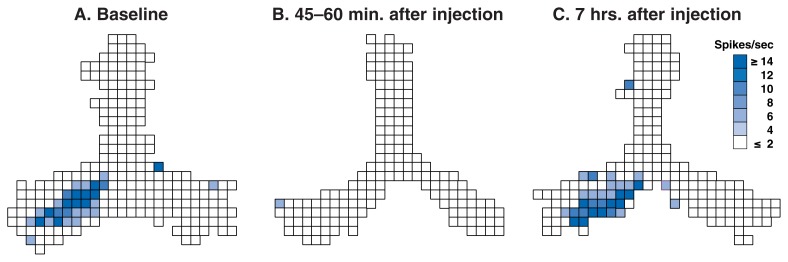
Figure 3.
Alcohol suppresses hippocampal pyramidal cell activity in an awake, freely behaving rat. Pyramidal cells often fire when the animal is in discrete regions of its environment, earning them the title “place-cells.” The specific areas of the environment where these cells fire are referred to as place-fields. The figure shows the activity of an individual pyramidal cell before alcohol administration (baseline), 45 to 60 minutes after alcohol administration, and 7 hours after alcohol administration (1.5 g/kg). Each frame in the figure shows the firing rate and firing location of the cell across a 15-minute block of time during which the rat was foraging for food on a symmetric, Y-shaped maze. White pixels are pixels in which the cell fired at very low rates, and darker colors represent higher firing rates (see key to the right of figure). As is clear from a comparison of activity during baseline and 45 to 60 minutes after alcohol administration, the activity of the cell was essentially shut off by alcohol. Neural activity returned to near normal levels within roughly 7 hours after alcohol administration.