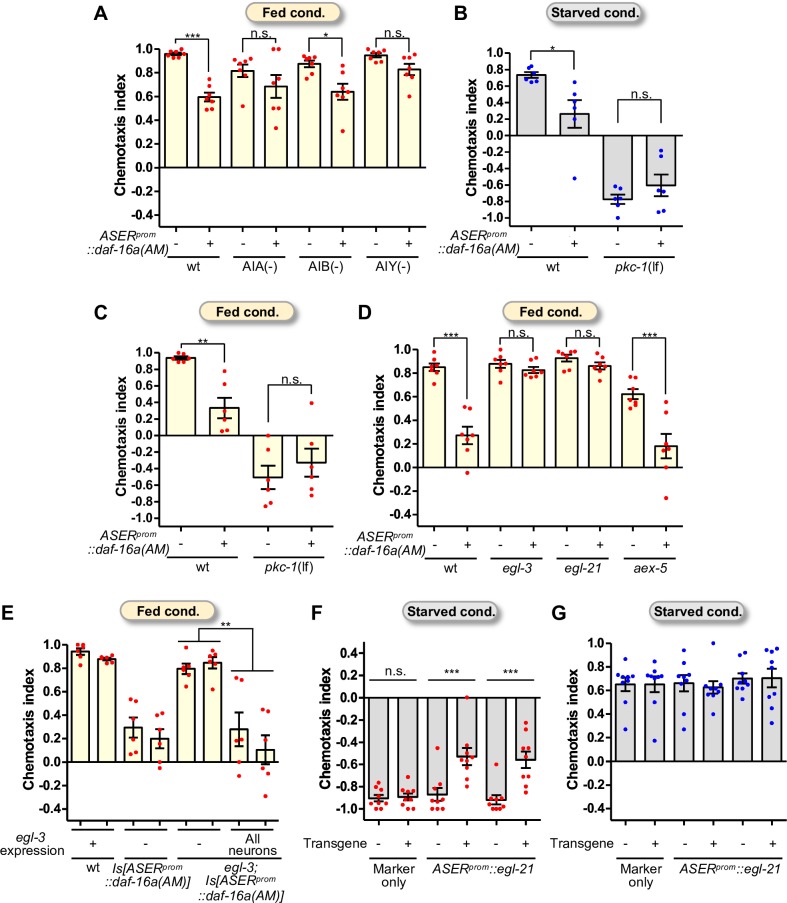
Fig 5. Neuropeptide signaling is required for DAF-16-dependent salt chemotaxis plasticity.
(A) The effect of DAF-16a(AM) on salt chemotaxis after high-salt/feeding conditioning in interneuron-ablated animals (N = 7). (B, C) The effect of DAF-16a(AM) on salt chemotaxis after low-salt/starvation (B) or high-salt/feeding (C) conditioning in pkc-1 loss-of-function mutants (N = 6). (D, E) Mutants of neuropeptide-processing enzymes (D; N = 7) and transgenic egl-3 mutant animals (E; N = 6). egl-3 cDNA was expressed by the pan-neuronal H20 promoter. (F, G) The effect of egl-21 expression in ASER on salt chemotaxis after high- or low-salt/starvation conditioning (N = 9). Two lines of egl-21 transgenic animals were used. Each dot in red (A, C, D-F) and blue (B, G) represents a chemotaxis index obtained from each trial after conditioning with high or low salt, respectively. Error bars indicate SEM. Tukey’s test following one-way ANOVA, n.s. p > 0.05, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.