Fig. 1.
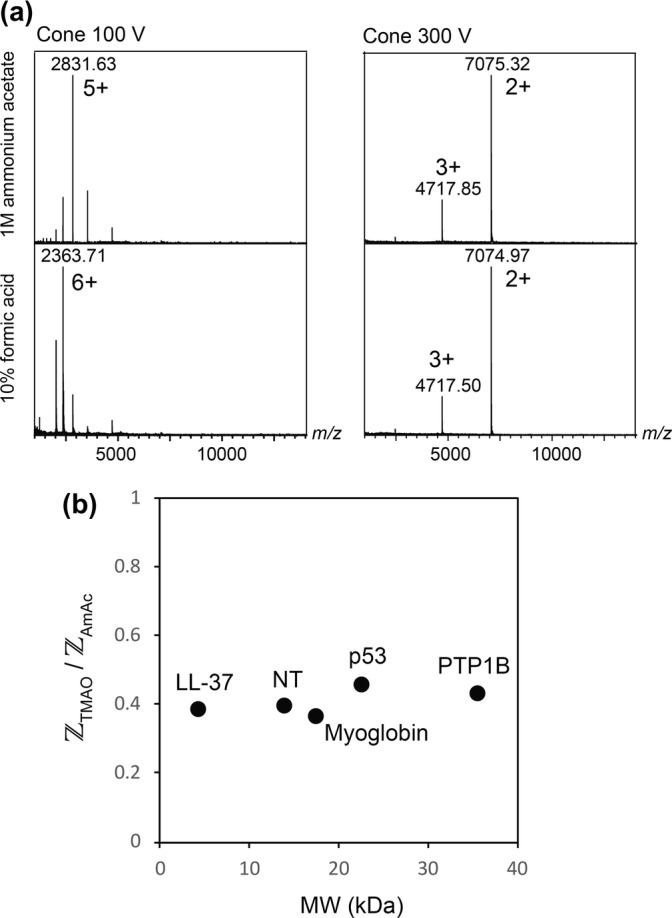
(a) TMAO charge-reduces above and below its pKa. Left: Mass spectra of NT in the presence of 100 mM TMAO in 1 M ammonium acetate, pH 7.5 (top) and in 10% formic acid (bottom) recorded at a cone voltage of 100 V, with the m/z value and charge state indicated for the most intense peak. Right: Increasing the cone voltage to 300 V to provide enhanced collisional activation reduces the charge of NT to 2.3+ and 2.2+ in ammonium acetate and formic acid, respectively. (b) TMAO reduces the charge of proteins by approximately 60%, as shown by the ratios between the average charge in TMAO with maximum collisional activation (ZTMAO), and the average charge in ammonium acetate, pH 7.5, without activation (ZAmAc). p53, p53 DNA-binding domain; PTP1B, phosphotyrosine phosphatase 1B
