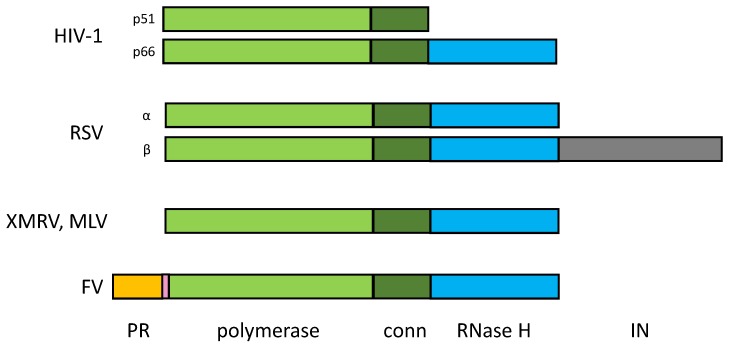
Figure 2.
Domain organisation of retroviral RTs. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase (RT) is a heterodimer with a 66-kDa and a 51-kDa subunit. The sequence of the N-terminal region of the two subunits is identical, and comprises the polymerase domain and the connection subdomain, which are highlighted in light and dark green, respectively. The RNase H domain (blue) is located at the C-terminus of the larger subunit. The Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) RT is also heterodimeric. The larger β subunit (95 kDa) carries, in addition to the polymerase, connection, and the RNase H (sub-)domains of the small α subunit (63 kDa), the IN domain (grey). Xenotropic murine leukaemia virus-related virus (XMRV) and murine leukemia virus (MLV) RTs are monomeric enzymes (75 kDa). In addition, the mature monomeric FV enzyme (86 kDa) harbors the PR domain. The stretch ranging from amino acids (aas) 102–143 between the C-terminal end of the PR domain, and the start of the RT domain is highlighted in pink.