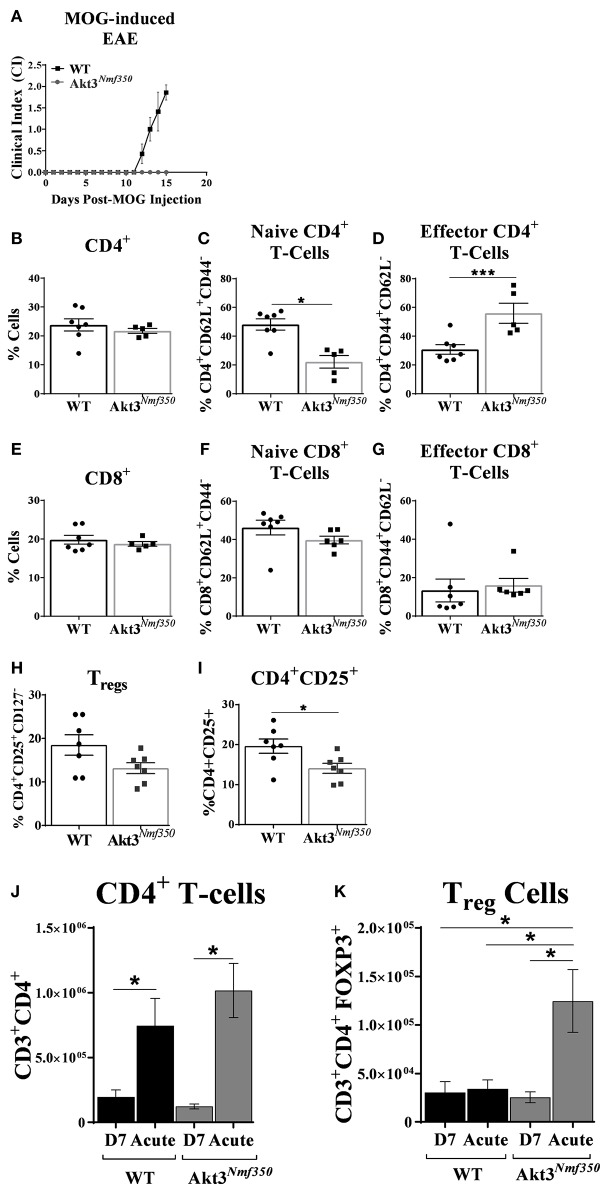
Figure 4.
Deep cervical lymph nodes of Akt3Nmf350 mice have significantly more effector T-cells before the onset of EAE symptoms, whereas draining inguinal lymph nodes have significantly more Tregs during acute EAE. (A) EAE disease course of Akt3Nmf350 (n = 11) vs. WT (n = 14) mice. Mice were euthanized at 13–15 days post-MOG injection and single cell suspensions from the deep cervical lymph nodes (dCLN) were isolated for FACS analysis. (B) Comparison of the %CD4+ cells present in dCLN of WT vs. Akt3Nmf350 mice, (C) CD4+CD62L+ naïve and (D) CD4+CD44+ effector T-cell subsets. (E) No differences were observed in the %CD8+ cells, (F) CD8+CD62L+ naïve or (G) CD8+CD44+ effector T-cells in dCLN of WT vs. Akt3Nmf350. (H) Tregs (CD4+CD25+CD127−) remained unchanged; (I) while the percentage of cells co-expressing CD4+ and CD25+ was significantly lower in Akt3Nmf350. (J) Total CD3+CD4+ T-cells, and (K) CD3+CD4+FOXP3+ cells in the inguinal LN (iLN) of WT and Akt3Nmf350 mice during preclinical (D7 post-MOG immunization) and acute EAE (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, Mann-Whitney U-test).