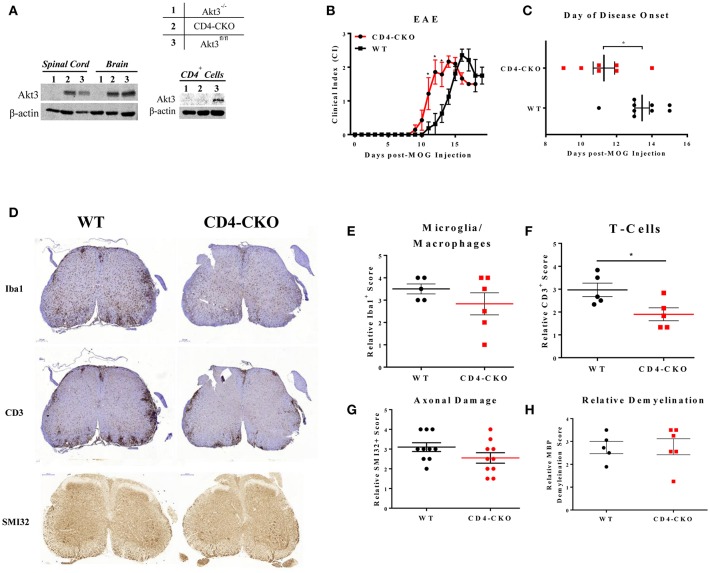
Figure 6.
Conditional knockout of Akt3 in CD4+ T-cells results in earlier disease onset during MOG-induced EAE. (A) Western blot analysis of protein homogenates of lymph node CD4+ T-cells, brain, and spinal cord isolated from (1) Akt3−/−, (2) CD4-CKO, and (3) Akt3fl/fl. Densitometry analysis of CD4-CKO and Akt3fl/fl brain and spinal cord homogenates yielded approximately equal ratios of Akt3/β-actin. (B) EAE clinical course and (C) day of disease onset (CI ≥ 1) of CD4-CKO mice (n = 7) and Akt3fl/fl (n = 9), representative graph of 4 independent experiments. (D) Histological analysis of microglia/macrophages (Iba1)—quantified in (E), T-cell infiltrates (CD3)—quantified in (F), axonal damage (SMI32) quantified in (G), and (H) demyelination (MBP) in lumbar spinal cord of CD4-CKO and Akt3fl/fl controls after 5 consecutive days with clinical scores (*p < 0.05, Mann-Whitney U-test). Scale bars = 200 μm.