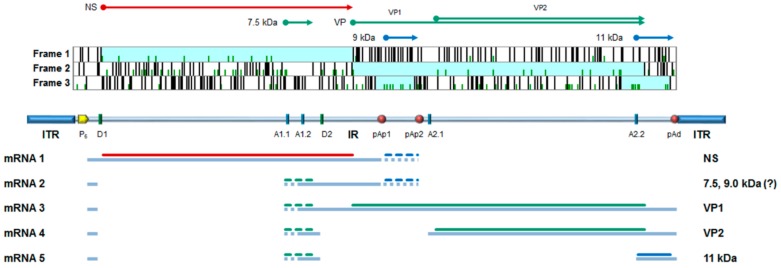
Figure 1.
B19V genome organization. Top: major open reading frames identified in the positive strand of genome; arrows indicate the coding sequences for the viral proteins. NS, non-structural protein; VP, structural proteins, colinear VP1 and VP2, assembled in a T = 1 icosahedral capsid; and 7.5 kDa, 9.0 kDa, and 11 kDa: minor non-structural proteins. Center: a schematic diagram of B19V genome indicating the two inverted terminal regions (ITR), and the internal region (IR) with the distribution of cis-acting functional sites (P6, promoter; pAp1, pAp2, proximal cleavage-polyadenylation sites; pAd, distal cleavage-polyadenylation site; D1 and D2, splice donor sites; A1.1, A1.2, A2.1, and A2.2, splice acceptor sites). Bottom: simplified transcription map of B19V genome, indicating the five classes of mRNAs (mRNA 1–5) with respective alternative splicing/cleavage forms (dashed), and their coding potential. Adapted from Reference [5].