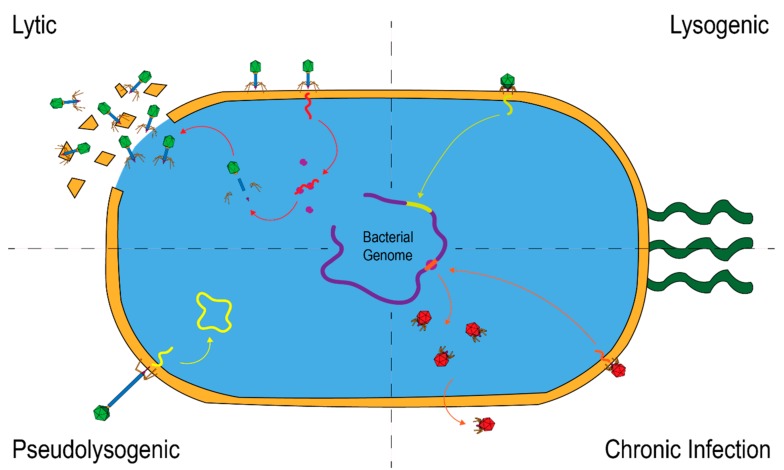
Figure 1.
An illustration of the four most well-studied phage lifecycles. Lytic lifecycles involve active replication of the phage and eventual lysis of host bacteria. Lysogenic phages integrate into the host genome or insert as plasmids and do not replicate. Chronic infection produces viral progeny but does not lyse the cell. Phages in a pseudolysogenic state insert DNA, which remains circularized in the cytoplasm.