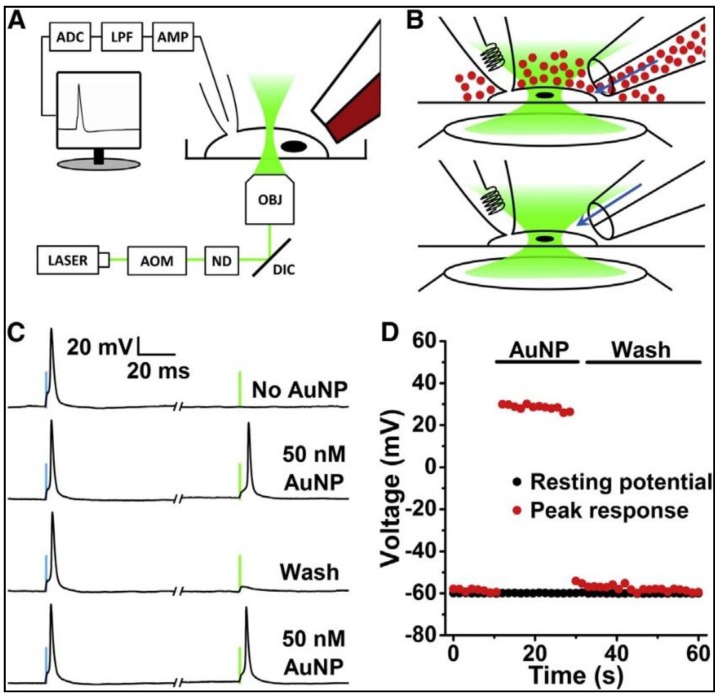
Figure 7.
Action potentials were stimulated by a 532-nm laser when the cells were incubated with AuNPs. (A) Diagram of the experimental setup (not to scale). The cell was patch-clamped in a whole-cell configuration (pipette on the left) and adding AuNP and perfusion-washing the cells were performed via the theta capillary (right). (B) AuNPs were perfused over a patch-clamped DRG neuron through one side of a theta capillary. After a satisfactory optical response was observed, fresh buffer was poured over the cell from the other side of the capillary to wash off the AuNPs. (C) Representative traces of current-clamped DRG cells firing action potentials, caused by 2 stimuli: A 300-pA, 1-ms current injection (left, blue bars) and a 174-mW, 1-ms, 532-nm laser pulse (right, green bars). At first, cells only responded to the electrical stimulus, but the addition of AuNPs made the cells sensitive to light. Washing removed enough AuNPs from the cell to prevent the laser from triggering an action potential. The cells regained their optical sensitivity when a second dose of AuNPs was added to the bath. (D) The washing showed that the laser effect relies on having a sufficient AuNP concentration near the cell. After the cells were washed, the laser effect vanished in seconds. Abbreviations: AOM: acousto-optic modulator; ND: Neutral density filters; DIC: dichroic mirror; OBJ: Microscope objective; AMP: Amplifier; LPF: Low-pass filter; ADC: Analog-to-digital converter. Reproduced with permission from [38]. Elsevier, 2015.