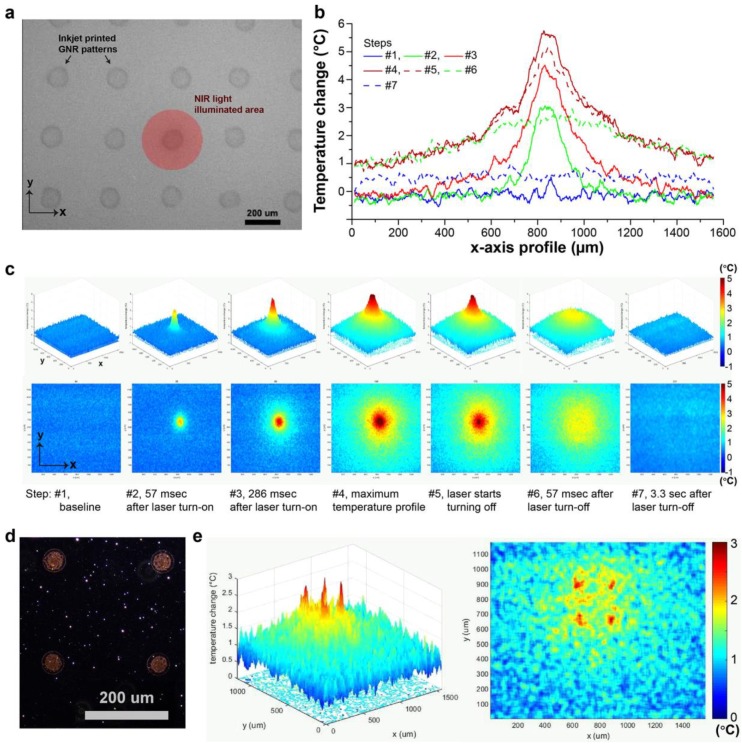
Figure 13.
Heat generation by inkjet-printed micro-thermo-plasmonic (μTP) heaters. (a) Experimental setup: inkjet-printed GNR μTP pattern array on PAH+-coated glass coverslip via a 50-μm inkjet nozzle with 350-μm drop spacing. An 808-nm NIR laser with a 1.38 W/mm2 power density is illuminated only on a single dot pattern. Image spatial resolution: 2.4 μm/px. (b,c) 2D and 3D profiles of temperature change around a μTP heater in (a). Gaussian profile heat source formed within 300 ms after the NIR laser was turned on (step 3); the overall temperature increased due to heat dissipation from the heater (step 3 to 4), and the heat source rapidly vanished when the laser was turned off (steps 5, 6). (d,e) Smaller μTP heaters (dark-field image) and their heat profiles at their highest temperature change (diameter: 45 μm, drop spacing: 250 μm, inkjet nozzle: 30 μm, droplet volume: ~5 pL, NIR laser power density: 1.16 W/mm2). Reproduced with permission from [18]. American Chemical Society, 2018.