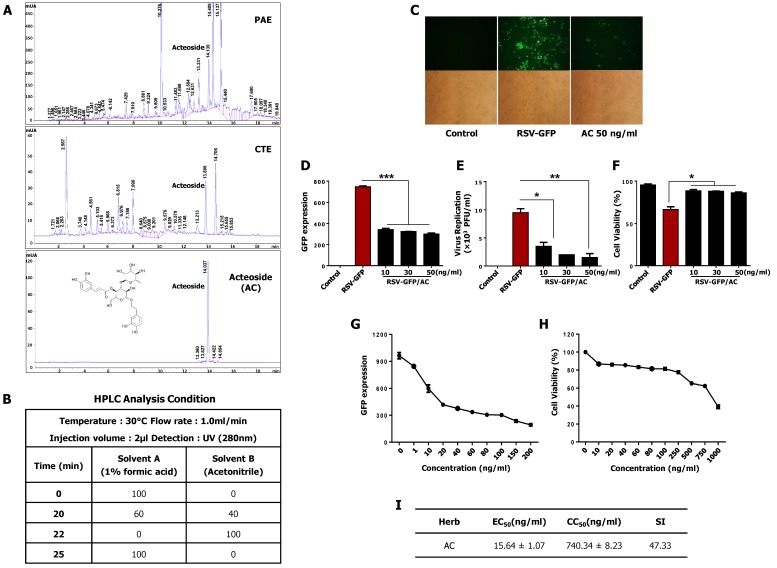
Figure 5.
Identification and antiviral effect of acteoside (AC) in-vitro. (A,B) Chemical compounds in PAE and CTE were analyzed by the reversed phase HPLC. The monolayer of HEp2 cells was infected with RSV-GFP (0.1MOI) for 2 h with DMEM containing 1% FBS. Then, the medium was replaced with DMEM containing 10% FBS and cells were treated with 10, 30, 50 (ng/mL) AC. (C) After 48 h, images were obtained (200× magnification). (D) GFP absorbance levels were measured by Gloma multi-detection luminometer (Promega). (E) Viruses were titrated from the cell supernatant and cells by standard plaque assay. (F) Cell viability was determined by trypan blue exclusion assay at 48 hpi. (A) HEp2 cells were infected with RSV-GFP (O.1MOI) for 2 h with DMEM containing 1% FBS. Then, the medium was changed to DMEM containing 10% FBS and cells were treated with various concentrations AC. 48 hpi GFP expression level was determined. (G) HEp2 cells were treated with various concentrations of AC and cell viability was determined at 48 hpi by cell cytotoxicity assay kit. (H) To calculate EC50 value, 50% reduction of GFP expression was considered as equivalent to the 50% reduction in virus titer. (I) The ratio between CC50 and EC50 considered as Selectivity Index (SI). GFP absorbance, cell viability and virus titer expressed as mean ± SD. Error bars indicate the range of values obtained from counting duplicate in three independent experiments. In vivo experiment was performed in duplicate. (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 regarded as significant difference).